Transport System SS2 Biology Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Transport System
Transportation is the movement of metabolic materials from various parts of an organism where they are produced and transported to other parts where such are used, stored or removed from the body.
NEED FOR TRANSPORT SYSTEM
All living organisms (plants and animals) need transport systems for the following reasons:
- To obtain essential materials such as oxygen, water and nutrients.
- To remove metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide, urea, water, etc.
- For moving water and mineral salts from the soil through the roots to the various parts of the plant.
- For transfer of hormones from the production site to the site of action.
- For transfer of glucose to various parts of plants.
RELATING TRANSPORT IN LOWER ORGANISMS TO THAT IN HIGHER ORGANISM
| SN | TRANSPORT IN LOWER ORGANISMS | TRANSPORT IN HIGHER ORGANISMS |
| 1 | Substances are moved over a small distance. | Substances are moved over greater distances. |
| 2 | Transport is by simple diffusion. | Transport involves diffusion and other means. |
| 3 | Diffusion is enough because the surface area to volume ratio (A/V) is great. | An effusion transport system is necessary because the surface area to volume ratio (A/V) is too small. |
| 4 | Cells are not isolated. | Isolated groups of cells need to be connected. |
| 5 | Transport materials are small in quantity. | Transport materials are large in quantity. |
TRANSPORT MATERIALS IN ANIMALS
| SN | MATERIALS TRANSPORTED | SOURCE | DESTINATION |
| 1 | Oxygen | Lungs | All living cells in the body |
| 2 | Carbon dioxide | Body cells | Lungs |
| 3 | Urea | Body cells | Liver |
| 4 | Excess salt | Body cells | Skin and kidney |
| 5 | Water | Body cells | Skin, lungs, liver, kidney etc |
| 6 | Amino acid | Small intestine | Body cells |
| 7 | Vitamins | Small intestine | Body cells |
| 8 | Sugar | Body cells | Body cells |
| 9 | Fatty acids and glycerol | Small intestine | Body cells |
| 10 | Mineral salt | Small intestine | Body cells |
| 11 | Hormones | Endocrine glands | Target organs of tissue |
| 12 | Antibodies | White blood cell | All body parts |
TRANSPORT MATERIALS IN PLANTS
| SN | MATERIALS TRANSPORTED | SOURCE | DESTINATION |
| 1 | Manufactured foods | Leaves | All body cells |
| 2 | Excretory products (C02 and water) | All living cells | Site of excretion e.g. stomata |
| 3 | Water (absorbed) | Soil | Leaves and other parts of the leaves |
Other materials transported in plants are:
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen waste products (latex)
- Amino acids
- Glucose
- Lipids
- Auxins (hormones)
- Mineral salts
TRANSPORT MEDIA
Liquid or fluid is usually the medium of transportation of minerals. Generally speaking, the four major media of transportation in organisms are:
- Cytoplasm: Used in lower unicellular organisms such as amoeba, chlamydomonas, euglena, etc.
- Cell sap/ Latex: A concentrated solution in the cell vacuole of plants.
- Blood: Used in most animals, especially vertebrates for conveyance of essential materials like oxygen, digested food, etc.
- Lymph: Found in higher animals. Lymph is a fluid with extra lymphocytes (W.B.C. with no red blood cells present). It returns its fluid to the main vein through an opening in the subclavian (left jugular) vein below the neck. Lacteal is a lymphatic vessel transporting fatty acids and glycerol. The lymph movement is enhanced by muscular action. It moves through lymph vessels. Some swellings exist in the gut along the lymphatic vessels, especially in the neck, groin and armpit called lymph nodes. These are where lymph passes through to be purified before entering into the bloodstream. Unlike the circulatory system, the lymphatic system ends blindly.
DIVERSE MECHANISMS OF TRANSPORTATION IN SOME ORGANISMS
- Unicellular Organisms: Materials are transported through continuous streaming movements. The streaming could be along the direction of movement of the organism, back to front (e.g. Amoeba) or in circular motion (e.g. Paramecium)
- Multicellular Organism: E.g:
i. Hydra: The movement of the gut wall draws water into the gut and causes digested food and oxygen within it to circulate. Thus the cell lining the gut absorbs the materials. The whopping movement of the flagella of flagellated cells also helps in material circulation in the gut.
ii. Flatworms: The large body surface area to volume ratio and extensive branching gut throughout the body make the food and oxygen diffuse into all the body cells. Movement of the body wall assists in transporting waste products out of the body.
iii. Insects and molluscs: Both have an open circulatory system i.e. the heart pumps blood out into a blood vessel with branches open into spaces in the body cavity known as Haemocoels. Blood from these spaces eventually flows into the vessels leading into the heart. Blood flow is unidirectional and blood distribution is poorly controlled.
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN MAMMALS (MAN)
The media of transportation in man include the blood and lymph.
i. Composition And Structure Of Blood
The blood is a tissue in a fluid form. It is about 5-6 litres in the body. Blood is made of two major components. The blood cells (corpuscles); are solid.The plasma which; is liquid.

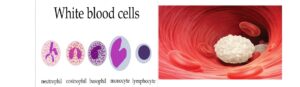
BLOOD CELLS
There are three types:
- Red blood cells (erythrocyte)
- White blood cells (leucocytes)
- Blood platelets (thrombocytes)
| SN | BLOOD CELLS | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION |
| 1 | RBC | i. Small, round and disc-like in shape.
ii. Has no nucleus. iii. One cubic litre of blood has about 5.5 million red blood cells. iv. Has a life span of about 120 days |
i. Helps to transport oxygen from the lungs to the body cells through its pigment (haemoglobin).
ii. Haemoglobin combines readily with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin in the lungs |
| 2 | WBC | i. Irregular (i.e. amoeboid in shape).
ii. Relatively large and colourless (larger than RBC but fewer).
iii. Contain nucleus- about 5,000-10,000 per pin head of blood (cubic millilitre of blood) |
i. Help to defend the body against diseases by engulfing and intruding pathogens (bacteria and viruses) or by secreting antibodies. |
White blood cells are of two types;
- Phagocytes- found in the lymphatic system which ingests bacteria, viruses and dead cells to prevent diseases in a process called phagocytosis.
- Lymphocytes- made in lymph glands and they produce antibodies i.e. chemicals which stick to the surface of germs to kill them.
| SN | BLOOD CELL | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION |
| 1 | Platelets | i. Tiny, Irregular all fragments.
ii. Have no nucleus. iii. Fewer in number and smaller in size than RBC. iv. About 250,000 – 400,000 per cubic ml of blood. v. Produced in red bone marrow. |
Aids in blood clotting |
| 2 | Blood Plasma | i. Liquid component of blood.
ii. A pale yellow liquid made up mainly of water (about 90% water) together with other dissolved substances like plasma proteins antibodies, hormones, enzymes, gases, digested food, salts and other waste products |
Transport the dissolved substances and the blood cells. |
| 3 | Lymph | i. A colourless liquid in the lymphatic system that has a similar composition to the tissue fluid but contains extra lymphocytes.
ii. Has no red cell |
i. Body defence by producing white blood cells. Disease-causing microorganisms found in the lymph are pushed out in the lymph node and engulfed by phagocytes.
ii. Absorption of fatty acid and glycerol |
FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD
- Oxygen is transported through hemoglobin.
- Temperature regulation by evenly distributing heat produced in the liver and the muscles throughout the body.
- Transportation of digested food (glucose, amino acid, fatty acids and glycerol) from the villi to all body cells and tissues for use or storage.
- Transportation of excretory products (C02, water, urea) from the site of production to excretory organs like skin, lungs, liver and kidney for removal
- Transfer of hormones from the production site to target organs.
- Transportation of water (90% of the blood content) to various cells for metabolic activities.
- Defense against infection through the action of WBC
- Blood clotting is initiated by the platelets when the injury is sustained
- Production of antibodies by the WBC for destroying pathogens and their harmful product.
ASSIGNMENT
- The following are true except one about transport in amoeba A. substances are removed over greater distance B. transport is by simple diffusion C. diffusion is enough for transport D. substances are moved over short distance
- The following metabolic materials are transported from body cells to the skin and kidney A. sugar B. hormones C. excess salt D. protein
- The transport medium which plays active roles in the defence and metabolism of lipids is … A. cytoplasm B. lymph C. blood D. platelets
- The following animals except one have an open circulatory system A. goat B. house fly C. snail D. grasshopper.
- One of the following has a nucleus A. red blood cell B. white blood cells C. platelets D. hydra