Reproductive System In Vertebrates SS2 Biology Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Reproductive System In Vertebrates
Most multicellular animals and plants undergo a complex form of sexual reproduction in which especially differentiated male and female reproductive cells (gametes) unite to form a single cell, known as a zygote, which later undergoes successive divisions to form a new organism. The process takes place with the help of the system known as the reproductive system. This system can be divided into
- male reproductive system and
- female reproductive system.
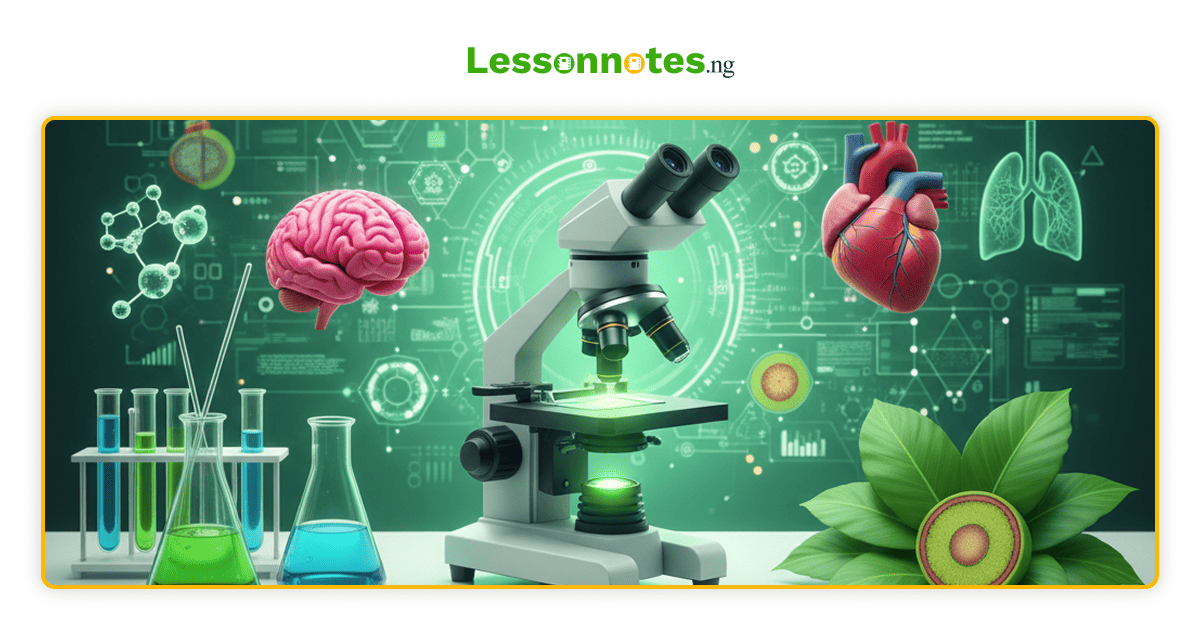
STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS OF THE MALE REPRODUCTION SYSTEM IN MAMMALS
| SN | STRUCTURE | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION |
| 1 | Testis | Oval-shaped, found in scrotal sacs in pairs outside the body to enjoy cooler temperatures. | i. production of sperms
ii. production of male sex hormones (testosterone) iii. development of secondary sexual character in male |
| 2 | Seminiferous tubules | Found within the testis, composed of a mass of sperm-producing tubes. | Site of sperm production |
| 3 | Epididymis | Found outside the testis as a long coiled tube. | Collect and store sperm temporarily till maturity. |
| 4 | Vas deferens (sperm duct) | A narrow tube leads from the epididymis to the seminal vesicles. | Conduction of sperm from epididymis to seminal vesicle. |
| 5 | Seminal Vesicle | A small sac at the back of the vas deferens. | i. Stores sperm till ejaculation.
ii. Secretes part of the seminal fluid. NOTE: Seminal fluid contains fructose which provides energy for the sperms. |
| 6 | Prostrate gland | Connected to the urethra through many tubules | Secretion of seminal fluid. |
| 7 | Cowper’s gland | Located very close to the prostate gland. | Secretes a part of the seminal fluid which raises the acidic pH of the female reproductive medium which otherwise can kill the sperm. |
| 8 | Urethra | A narrow tube which passes through the penis. | Aids is the passage of sperm into the vagina of the female animal and also the passage of urine out of the body hence it is called the urinogenital opening. |
| 9 | Penis | Contains tissues which make it turgid (erect when filled) with blood | Helps to introduce sperm into the vagina of the female animal and also the passage of urine. |
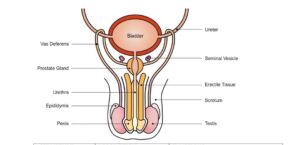
STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
| SN | STRUCTURE | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTIONS |
| 1 | Ovaries | Found on each side of the vertebra column (two in every woman) | i. Produce eggs (ova)
ii. produces female sex hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) iii. Development of secondary sexual characters in females. |
| 2 | Oviduct (Fallopian Tube) | A long narrow tube funnel opening which receives eggs released by the ovary and it is a linkage between the ovary and uterus. | i. Fertilization takes place in the oviduct.
ii. Allows the passage of an egg from the ovary to the uterus. |
| 3 | Uterus | A muscular organ is a cavity for the development of the zygote into a baby. | i. Site of embryo development from implantation till birth |
| 4 | Vagina | A muscular tube leads from the uterus to the outside of the body. | i. It receives sperm from the penis during intercourse
ii. Allows the passage of the foetus during birth |
| 5 | Cervix | A ring of muscles with a tiny opening that closes the lower end of the uterus where it joins the vagina. | Controls the opening and closing of the vagina especially during birth. |
| 6 | Vulva | Refers to all external parts of the female reproductive organ | i. Allows the passage of the penis into the vagina during intercourse.
ii. permits passage of foetus during birth. |
| 7 | Clitoris | A small sensitive organ which corresponds to the male penis. It is erectile and becomes stiff when stimulated due to blood inflow | i. Helps to stimulate females during sexual intercourse(experience orgasm) |
STRUCTURE OF MAMMALIAN GAMETES
WHAT IS A GAMETE?
A gamete is a mature sexual reproductive cell having a single set of unpaired chromosomes. It can be a male or female gamete. They are formed in the gonads (testis on ovaries) through a process called gametogenesis.
MALE GAMETE
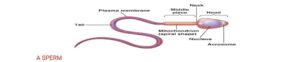
A SPERM
This is called sperm (or spermatozoa) and is produced in the male gonads (testis) by a process called spermatogenesis. It is microscopic and unicellular. Usually smaller and more elongated than the egg; about 0.05 mm (0.005 cm) long.
Spermatozoon consists of the following parts:
i. Acrosome: It can be found at the upper part of the head, containing lytic enzymes used to dissolve egg membranes to enhance penetration during fertilization.
ii. Middle piece: It contains mitochondria for the generation of energy used by the sperm for swimming towards the egg.
iii. Flagellum: The long whip-like tail for propelling the sperm cell
iv. Nucleus: It can be found in the head of the sperm cell containing genetic materials (DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid) which fuses with the nucleus of the ovum at fertilization.
FEMALE GAMETE

THE OVUM
This is called an egg (ovum) and is produced in the female gonad (ovary) by a process called oogenesis. This is larger than sperm, about 0.1mm in diameter.
Each ovum is made up of the following:
i. Cytoplasm
ii. A central Nucleus: It contains the chromosomes which carry the genes.
iii. Granules and yolk droplets: A source of nourishment for the embryo at the early stage of development.
iv. Plasma membrane: It surrounds the cytoplasm.
v. Outer vitelline membrane and jelly coat of glycoprotein.
Note: The nuclei of the sperm and ovum contain chromosome which carries the genes that are responsible for the transmission of characters from parents to offspring.