Regulation Of Internal Environment II SS3 Biology Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Regulation Of Internal Environment II
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
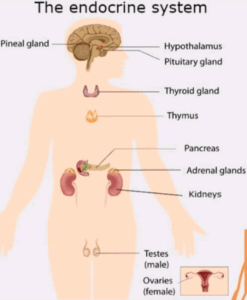
The endocrine system is a group of ductless glands whose products pass directly to the surrounding blood vessels. These secretions called hormones or chemical messengers circulate to parts of the body where they stimulate the body to act in a certain way.
FUNCTIONS OF HORMONES
- Stimulate growth and development.
- Stimulate the basic rate at which the body works i.e. metabolism. All endocrine glands are under the control of pituitary glands in the midbrain.
- Thyroid Gland: Butterfly-shaped, found in the neck, secretes hormone thyroxine which controls the basal metabolic rate of the body(the rate at which oxygen and food are utilised by the body tissues and this affects physical and mental growth. Too much thyroxine secretion results in a disease called exophthalmic goitre characterised by bulging eyes and over reactiveness.Deficiency of thyroxine early in life results in CRETIN(retarded mental and physical growth.If the thyroid gland malfunctions later in life and the thyroxine level is Inadequate, MYXOEDEMA results which are characterised by overweight, inactivity, and sensitivity to cold. Iodine is needed to make thyroxine where water lacks Iodine, the goitre may appear and this is the stimulation of the thyroid gland to grow bigger to compensate for insufficient iodine.
ISLETS OF LANGERHANS
These cells are not connected to pancreatic ducts but are produced by special cells in the pancreas. They produce the hormone INSULIN which regulates the level of blood glucose by controlling the rate at which glucose is taken up from the blood by surrounding tissues. If the insulin level is low, glucose is not taken into the tissues but appears in the urine and is lost from the body, a diabetic not receiving regular insulin injections may fall into a diabetic coma, i.e. brain cells are not receiving any glucose.
ADRENAL GLAND: They are situated above each kidney. They contain two tissues, the adrenal medulla (inner tissue )produces adrenaline which works with sympathetic nerves ANS.it is produced in stress and prepares the body for action by increasing breathing rate, raising blood sugar level, and increasing heartbeat rate. Muscles are toned and blood is directed to where needed most e.g leg muscles if running away, skin if one is getting hot
OVARIES: Ovaries produce the hormone oestrogen which controls the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as the development of mammary glands, hair under the armpit and groin, and widening of the hip. Ovaries produce progesterone which prepares the lining of the uterus to be ready for receiving a fertilised egg for implantation and for continuing pregnancy to full term and changes. If no pregnancy occurs progesterone production is stopped by the ovary thus monthly menstrual cycle starts again
THE TESTIS: Testes produce the hormone testosterone which controls the male secondary sexual characteristics e.g. growth of hair on the face, armpit, and groin, increased muscle development, deepening of the voice, and penis /scrotum enlargement.
Both oestrogen and progesterone promote growth and lead to arousal of interest in the opposite sex. Underdevelopment of either hormone results in underdevelopment of sexual organs and a lack of interest in the opposite sex
DISEASES OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- Dwarfism: Thyroid deficiency
- Cretinism: Thyroid deficiency in childhood
- Diabetes: Insulin deficiency
- Goitre: over secretion of thyroxin





















