Terminologies In 3 dimensional Art SS1 Visual Arts Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Terminologies In 3 dimensional Art
3D art refers to artwork that has three dimensions: height, width, and depth. Unlike 2D art (which is flat), 3D art exists in physical space and can be viewed from multiple angles.
Examples of 3D art include sculptures, installations, ceramics, and architecture.
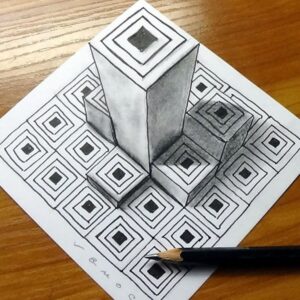
KEY TERMINOLOGIES IN 3D ART
- Form: Form refers to the shape and structure of an object in 3D space. It is the most important element in 3D art because it defines the object’s appearance from every angle. Forms can be geometric (like cubes and spheres) or organic (natural and irregular shapes, such as the human body or a tree).
- Volume: Volume refers to the amount of space that an object occupies. In 3D art, the volume helps us understand the size and mass of the artwork. Artists manipulate volume to create large or small forms depending on the effect they want to achieve.
- Mass: Mass is closely related to volume. It refers to the physical bulk or weight of a 3D object. Even if the material is light, the mass can be visually heavy, meaning the object looks solid and dense.
- Space: Space refers to the area around, between, and within objects in a 3D artwork. There are two types of space in 3D art: positive space(the area occupied by the object) and negative space(the space around and through the object). Artists use space to create a sense of balance and harmony in their works.
- Texture: Texture in 3D art refers to the surface quality of an object—how it feels to the touch or how it looks like it would feel. Textures can be real (actual texture) or implied (visual texture). Sculptors use texture to add interest and detail to their work.
- Balance: Balance is the arrangement of elements in a 3D artwork to create a sense of stability. There are three types of balance:
i. Symmetrical Balance: Both sides of the artwork are identical or nearly identical.
ii. Asymmetrical Balance: Both sides are different but still balanced.
iii. Radial Balance: Elements radiate from a central point.
- Proportion: Proportion refers to the relationship between the size of different parts of an object. Correct proportions create realism, while exaggerated proportions can express emotions or ideas.
- Perspective: Perspective in 3D art involves creating the illusion of depth and distance. Artists use techniques like linear perspective(lines converging to a point) or atmospheric perspective (fading colours or details) to show depth.
- Armature: An armature is a framework used to support and give structure to sculptures, especially when working with soft materials like clay or plaster. It helps the artwork keep its shape until the material hardens.
- Relief: Relief is a type of sculpture where the forms project from a flat surface. There are two types:
i. High relief (alto-relievo): The forms stand out significantly from the background.
ii. Low relief (bas-relief): The forms are shallow and do not stand out as much.

EXAMPLES OF 3D ART FORMS
- Sculpture: The art of making objects by carving, modelling, or assembling materials like clay, stone, metal, or wood.
- Ceramics: Creating objects like pots, vases, or figurines using clay and then firing them in a kiln.
- Architecture: Designing and constructing buildings and other large structures.
- Installations: Large-scale artworks that transform a space, often including different materials and interactive elements.
ASSIGNMENT
Look for an example of a sculpture in your environment. Write a short description of its form, texture, and space.











