Marketing Mix II – Marketing Environment SS1 Marketing Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Marketing Mix II – Marketing Environment
The marketing environment is a term that is used to collectively identify all the elements that have some impact on the actual performance of a market. This includes events and factors that occur within the context of the market itself and also any elements that are based outside the market. The idea behind defining the market environment is to understand what forces are exerting some amount of influence in the marketplace and understand why and how a market reacts to those forces in certain ways. The environments in which you will have to market your new product are a major factor in determining your strategy. In a real-life marketing (plan you would spend a solid amount of time researching these environments. The marketing environment is everything an organization must take into consideration when developing and presenting a new product.
FACTORS AFFECTING MARKETING ENVIRONMENT
The marketing environment is made up of factors and forces that influence marketing. These forces can be internal like departments (other than marketing such as the finance department and human resource department) or external like competitors, suppliers, and economic or political situations.
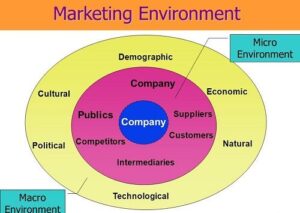
To understand them better, marketing personnel divide them into two categories: macro-environment and macro-environment.
- Micro-Environment: The micro-environment refers to the forces or factors that are close to the company and affect its ability to serve its customers. These factors are:
i. Political factors: These are laws, procedures, practices and policies formulated by the government to regulate and facilitate business activities. It also involves the stability or instability of the government.
ii. Cultural factors: These are ways of life of the people such as language, aesthetics and their perception. A marketer should learn to adjust to the culture of the people for him to operate successfully.
iii. Technological factors: These are changes or advancements in process equipment and devices that are used to accomplish the tasks of the marketing or an organization.
iv. Economic factors: These consist of inflation, national income and the economic system of a country. It also includes changes in the business cycle. A marketer should be able to adjust to such changes to operate successfully.
v. Social factors: These are values and norms of the society, interest groups, reference groups and social class. These factors influence the buying decisions of consumers.
vi. Suppliers: The suppliers to a firm can also alter its competitive position and www marketing capabilities. These are raw material suppliers, energy suppliers, and suppliers of labour and capital. The bargaining power of the supplier gets maximized in the following situations:
a) The seller firm is a monopoly or an oligopoly firm.
b) The supplier is not obliged to contend with other substitute products for sale to the buyer group.
c)The buyer is not an important customer.
d) The buyer is not an important customer
e) The supplier poses a real threat of forward integration.
vii. Market intermediaries: Every producer has to have several intermediaries for promoting, selling and distributing the goods and serving ultimate consumers. These intermediaries may be individual or business firms. These intermediaries are the middlemen (wholesalers, retailers, agents, etc.), distributing agencies, market service agencies and financial institutions.
viii. Customers: The customers may be classified as:
- Ultimate customers: These customers may be individuals and householders.
- Industrial customers: These customers are organizations which buy goods and services for producing other goods and services to fulfil other objectives.
- Resellers: They are the intermediaries who purchase goods to resell them at a profit. They can be wholesalers, retailers, distributors, etc.
- Government and other non-profit customers: These customers purchase goods and services and make them available to those for whom they are produced, for their consumption in most cases.
- International customers: These customers are individuals and organizations of other countries who buy goods and services either for consumption or for industrial use. Such buyers may be consumers, producers, resellers and governments.
- Competitors: Competitors are those who sell the goods and services of the same and similar description in the same market. Apart from competition on price, there is likely to be product differentiation. Therefore, it is necessary to build an efficient system of marketing. This will bring confidence and better results.
- Public: The company must satisfy the people at large along with its competitors and the consumers. It is necessary for future growth. The actions of the company do influence the other groups forming the general public for the company. A public is defined as ‘any group that has an actual or potential interest in or impact on a company’s ability to achieve its objective. Public relations are certainly a broad marketing operation which must be fully taken care of.
- Macro-Environment: The macro marketing environment takes into account all factors that can influence an organization, but are outside of their control. These are: political, economic, socio-cultural and technological.
i. The political environment: These are laws, procedures, practices and policies formulated by the government to regulate and facilitate business activities. It also involves the stability or instability of the government.
These include all laws, government agencies and lobbying groups that influence or restrict individuals or organizations. Marketers need to be aware of these restrictions as they can be complex.
Some products are regulated by both state and federal laws. There are even restrictions for some products as to who the target market may be. For example, cigarettes should not be marketed to younger children. There are also many restrictions on subliminal messages and monopolies. As laws and regulations change often, this is a very important aspect for a marketer to monitor.
ii. The economic environment: These consist of inflation, national income and the economic system of a country. It also includes changes in the business cycle. A marketer should be able to adjust to such changes to operate successfully.
It consists of all factors such as salary levels, credit trends and pricing patterns that affect consumers’ spending habits and purchasing power. This refers to the purchasing power of potential customers and how people spend their money. The four stages of the economic cycle through prosperity, recession, depression and recovery.
Consumers spend more during the prosperity stage than in the depression stage, which is when the lowest amount of consumer spending takes place. Your marketing campaign, product offerings and pricing must be taken into account for the current economic cycle to be successful.
iii. The social environment: These are values and norms of the society, interest groups, reference groups and social class. These factors influence the buying C decisions of consumers, including institutions and other forces that affect the basic values, behaviours, and preferences of society- all of which affect consumer marketing decisions
iv. The technological environment: These are changes or advancements in processes, equipment and devices that are used to accomplish the tasks of the marketer or an organization. It is perhaps one of the fastest-changing factors in the macro environment. This includes all developments from antibiotics and surgery to nuclear missiles and chemical weapons to automobiles and credit cards.
As these markets develop it can create new markets and new uses for products. It also requires a company to stay ahead of others and update its technology as it becomes outdated. They must be informed of trends so they can be part of the upcoming events rather than becoming outdated and suffering the consequences financially.
v. Cultural factors: These are ways of life of the people such as language, aesthetics and their perception. A marketer should learn to adjust to the culture of the people for him or her to operate successfully.