Trade – Retailers & Retail Trade SS1 Commerce Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Trade – Retailers & Retail Trade
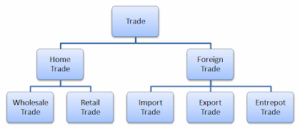
Trade (Trading) is the buying and selling of goods and services. It is divided into Home Trade and Foreign Trade.
Home Trade involves the exchange (i.e. buying and selling) of goods and services within a country and is subdivided into wholesale trade and retail trade.
-
RETAIL TRADE
Retail trade involves buying in small quantities from the wholesaler or the manufacturer and selling in units (bits or fractions) to the final consumers.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE RETAILER/RETAIL TRADE
- The retailer sells in units or fractions.
- The retailer stocks and sells a wide variety (range) of goods.
- They sell directly to the ultimate consumers.
- They buy in small quantities from the wholesaler or manufacturer.
- The wares consist of fast-selling products, mainly consumer goods.
- A large number of small shops are involved.
- They are the final link in the distribution chain.
- The majority of the goods they deal in are obtained from the wholesaler.
FUNCTIONS OF THE RETAILER
A: To the manufacturer:
- He sells the goods produced by the manufacturer to the final consumer.
- He helps in informing the manufacturer about the likes and dislikes of the consumers either directly or through the wholesalers.
- He advises the manufacturer.
B: To the Wholesaler:
- He provides information about consumer needs and changes in market trends to the wholesaler
- He advises the wholesaler
C: To the Consumer:
- Provision of a variety of goods
- Granting of credit to credit-worthy customers
- Provision of useful information and advice
- Breaking the bulk i.e. selling in smallest quantities (units) to the consumer
- Provision of after-sales services e.g. installation, servicing e.t.c
- Delivery of goods to the consumer door free of charge
- Preparing the goods for sale e.g. packing or re-packing the goods to different sizes to suit the needs of the consumers
- Giving personal attention to the consumer
- Guiding the consumer in making their choices
- Completing the process of production e.g. branding of goods
- The retailer advertises the goods.
- The retailer ensures door-to-door services i.e. he brings the goods nearer to the consumer
- Opening for business and selling at convenient
- Delivering goods to consumers on request
FACTORS TO BE CONSIDERED WHILE SETTING UP A RETAIL BUSINESS
i. Amount of capital available.
ii. Location (or the site) of the shop.
iii. Experience and knowledge of the retail job.
iv. Layout of the shop i.e. the plan or design of the shop must be attractive
v. Source of supply of the goods the retailer intends to deal in
vi. The pricing policy and terms of trade i.e. whether to grant discounts, credits or sell solely for cash;
vii. The type or nature of goods to be sold;
viii. The details of the operating plans e.g. hours of business, opening time, trading days etc;
ix. How records will be kept.
FACTORS A RETAILER SHOULD TAKE INTO CONSIDERATION WHEN MAKING HIS PURCHASES
- Quantity of goods to be bought.
- The extent of the credit facility available to him.
- Quality of goods must confirm consumers’ needs and tastes
- The terms of payment i.e. discount given
- The cost of transporting the goods
- The method of delivery of the goods to him e.g. through road, rail, sea etc
- Any additional charges for packing or off-loading the goods
REASONS WHY RETAIL BUSINESS MAY FAIL
a) Wrong purchases;
b) Poor recording-keeping techniques i.e. inability to keep proper accounting records;
c) Failure to insure the business;
d) Extravagance, overspending i.e. spending the business money on personal expenses;
e) Lack of experience or knowledge of the trade;
f) Poor credit administration i.e. indiscriminate granting of credit facilities to customers;
g) Inadequate capital for running the business and for expansion;
h) Competition from bigger businesses;
i) Inability to plan properly and forecast the future;
j) Insensitivity to current market trends.



















