Semiconductor(Electronics) Electrical Conduction through Solid Materials SS3 Physics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Semiconductor(Electronics) Electrical Conduction through Solid Materials
CONTENT
- Condition for discharge
- Characteristics of cathode rays and application
- Thermionic emission and application
- Diode valve/Cathode rays Oscilloscope
Condition for Discharge
Experiments with discharge tubes show that gases conduct electricity under low pressure and high potential difference. At very low pressure and high voltage, the gas in the discharge tube breaks into ions. The positive ions move towards the cathode, and the negative ions and free electrons move towards the anode. The positive ions knock off electrons from the metal plate of the cathode. The electrons produced at the cathode are called cathode rays.
EVALUATION
- Draw a discharge tube and explain how electricity is conducted through it.
- What are cathode rays?
Characteristics of Cathode rays
- They consist of streams of fast-moving electrons.
- They cause glass and other materials to glow or fluoresce with a greenish colour.
- They travel in straight lines
- They are deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
- They can ionise a gas
- They will turn a light paddle wheel in the tube because they have mass, momentum and energy.
- They are highly energetic particles.
- They can affect photographic plates
- They can produce x-rays from high-density metals when they are suddenly stopped by such metals.
- They are highly penetrating and can penetrate through metals such as aluminium, steel and gold foil.
Application of Cathode rays
One application of cathode rays is in fluorescent tubes used commercially for lighting and display signs. The tube contains mercury vapour, which at low pressure glows or fluoresces at the passage of cathode rays.
EVALUATION
- Mention at least five characteristics of cathode rays
- Describe how cathode rays are used in fluorescent lamps and the production of neon signs.
Thermionic Emission
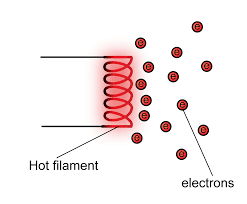
Whenever a metal is heated to a sufficiently high temperature, electrons are emitted from the surface of the metal in a process known as thermionic emission
When the filament is heated to a high temperature, extra energy given to its free electrons at the surface of the metal enables them to break through the surface of the metal and exist outside it as an ‘electron cloud’. This is the process of thermionic emission.
The diode valve is a simple application of the principle of thermionic emission. It consists of an anode, usually in the form of a cylinder, a hot filament (heater ) made of tungsten wire and components surrounding the filament. All these components are enclosed in a highly evacuated glass bulb.
The action of a diode, diode characteristics
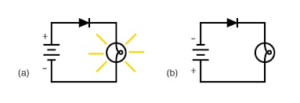
The filament supplies free electrons when heated by the current from the battery (E), when the anode is made positive in potential concerning the cathode, electrons
flow towards the anode and constitute the anode current (Ia) which is registered by the milli-ammeter.
Diode Characteristics
The diode characteristics curve shows that the diode valve does not obey Ohm’s law. That is why it is called a non-Ohmic conductor. Because the action of the diode allows current to flow only in one direction, the valve is used as a rectifier to produce d.c. voltage from an a.c supply.
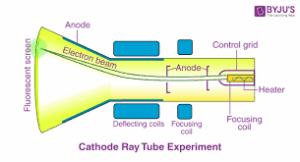
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
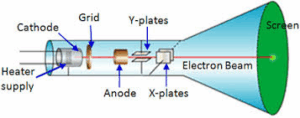
The cathode rays oscilloscope is an instrument used for the investigation of current voltages in electronic circuits. It is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun at one end, and a fluorescent screen at the other end. Between these are two pairs of deflector plates near the middle of the tube. The electron gun consists of (i) the heated filament, to supply electrons by thermionic emission, (ii) the anode (iii0 the cathode. The anode acts as a focusing lens to accelerate and focus the electron onto a spot in the fluorescent screen.
The cathode rays oscilloscope is used for studying all types of waveforms, especially the alternating current waveforms and to measure frequencies and amplitude of voltage of electronic devices.
GENERAL EVALUATION
- Define gravitational potential
- Define gravitational field
READING ASSIGNMENT
New School Physics for SSS page 481-483.
WEEKEND ASSIGNMENT
- When a metal is heated to a high temperature and electrons are emitted from its surface, this is known as ____ (a) photoelectric emission (b) Thermionic emission (c) field emission (d) secondary emission
- The term electrical discharge means (a) voltage is a gas (b) current in a liquid ( c) current in a gas (d) voltage.
- Which of the following is an application of glow discharge phenomena? (a) filament lamp (b) fluorescent lamp (c) cathode ray oscilloscope (d) electron microscope.
- Which of the following is an application of hot cathode emission? (a) filament lamp (b) cathode ray oscilloscope (c) electron telescope (d) Binoculars
- Which of the following contributed to conduction in a gas? (i) molecules (ii) electrons (iii) ions (A) I only (b) II only (c) I and III only (d) II and III only.
THEORY
- (a) Draw a labelled diagram of a cathode ray oscilloscope showing the essential parts
(b) What are the functions of (i) the hot filament (ii) the anode (iii) fluorescent screen (iv) deflector plates
(c) State one way in which cathode rays differ from electromagnetic waves
2. (a) Describe briefly how electrons can be liberated from i. a cold cathode ii. A hot cathode
(b) What is thermionic emission?