Calculating Distances Using Longitude, Latitude & Great Circles SS3 Mathematics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Calculating Distances Using Longitude, Latitude & Great Circles
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, the student should be able to:
- Give the formula for finding distance along the parallel of longitude or great circle.
- Solve problems involving longitude or great circles.
- give the formula for finding distance along the parallel of latitude
- Solve problems involving latitude
INSTRUCTIONAL RESOURCES Real globe and an Orange.B.
PRESENTATION:
The teacher presents the lesson with the steps below:
STEP I Identification of prior ideas.
Mode: Entire students
Teacher’s Activities: Displays instructional resources and instructs the students to identify the lines of longitude afterwards leads students to give the formula for determining distance along a parallel of longitude or great circle.
Students’ Activities: Students identify the lines on longitude and give the formula for determining the parallel of longitude or great circle.
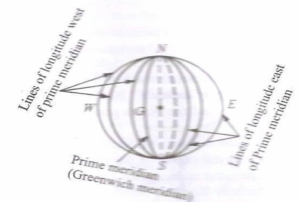
Lines of Longitudes
The formula for calculating distance along a parallel of longitude or great circle.
Distance. = ө/360 x 2πr cos latitude°
STEP II: Exploration
Mode: Individual
Teacher’s Activities: Leads students to solve problems involving longitude or great circle
Students’ Activities: Students solve problems involving longitude or great circle
Towns A and B lie on the equator. A has longitude 63° E. While B has longitude 123°E. What is the difference between the two towns along the equator?
- How far is Santa from the North Pole? (Take the radius of the Earth is 6400).
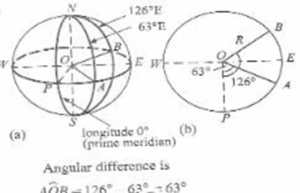
Arc AB = 63/360. x2πR. = 2 x 22 x 160 km = 7040 km
(b) distance from the North Pole = arc AN. The angular difference is 90°
Therefore, Arc AN = 90/360 x 2πR. = 90/360 x 2 x 22/7 x 6400 km = 10057 km.
STEP III: Discussion
Mode: Individual
Teacher’s Activities: Displays instructional resources and instructs the students to identify the lines of latitude afterwards leads students to give the formula for determining distance along parallel latitude.
Students’ Activities: Students identify the lines on latitude and give the formula for determining the parallel of latitude
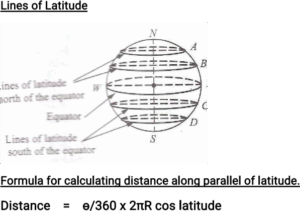
Where: ө is the angular difference, and cos latitude is the angle formed at the parallel of
22/
latitude and use R = 6400 km where not given. π = 7
STEP IV: Application
Mode: Individual
Teacher’s: Leads students to solve problems involving latitude.
Students’ Activities: Students solve problems involving latitude.
- Find the longitude difference between A( 06°N, 40°W) and B(60°N, 70°E)
- Find the distance measured along the parallel of latitude between A And B
( Take the radius of the Earth =l 6400 KM and π =22/7
- Calculate the difference in longitude between the following places
- P( 48° N, 25°E) and Q( 48°N, 58°E).
- X(65°S, 40°E) and Y(65°S, 32°W)
- Calculate the difference in latitude between the following places.
- P( 49°N, 50°E) and Q(30°S, 50°E).
- X( 60°N, 32°W) and Y(20°N, 32°W)
CONCLUSION: The teacher goes around to assess the student’s work and gives corrections on the board for students to copy.
ASSIGNMENT:
Calculate the distances between the places given in evaluation questions (a) and (b) above
REFERENCES:
- Bakare L. Niyi, 2014, Mathematics Clinic
- Essential Mathematics for SS 3 students.