Regulation Of Internal Environment I SS3 Biology Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Regulation Of Internal Environment I
Homeostasis: this can be defined as the maintenance of a fairly constant internal environment In an organism. Body fluids such as blood, lymph, and tissue fluids make up the internal environment of an organism. The internal environment must be kept fairly constant for the body cells’ healthy growth and efficient functioning.
ORGANS INVOLVED IN HOMEOSTASIS.
Parts of the body which are involved In homeostasis are:
- Kidneys.
- Ductless glands (hormones).
- Liver.
- Brain.
- Skin.
The brain has overall control of the homeostatic processes in the body.
THE KIDNEY.
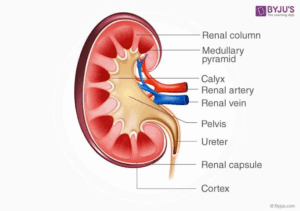
BYJU’S
- Renal column Medullary pyramid calyx
- Renal artery Renal Vein
- pelvis
- Ureter
- Renal capsule
- Cortex
The Mammalian kidney is a bean-shaped and reddish-brown organ located in the posterior end of the abdomen, The right kidney Is slightly lower in the body than the left. The kidney has two distinct regions – an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Over one million fine tubules called the urinary tubules pass through both areas.
They open at the tips of triangular-shaped masses of tissues called pyramids. The pyramids open into a funnel-web peed cavity called the pelvis, The kidney has many tiny capillaries which are branches of the renal artery and renal vein.
FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEYS.
The kidneys perform several functions among which are:
- Psm Regulation: This can be defined as the process by which an animal regulates the balance between water and salts in its body fluids.
- Excretion: The kidneys are also involved in the removal of metabolic waste products from the body in the form of urine,
- Maintenance of acid-base balance: The kidneys also maintain the acid-base balance in the body. When the concentration of the acids becomes more than the concentration of the bases, more acid is excreted by the Kidneys with the urine. If the concentration of a base becomes higher, more salts will be excreted with the urine.
DISEASES OF THE KIDNEYS
Diuresis: Diuresis is a condition in which the cells of the kidney tubules are not reabsorbing water from the glomerular filtrate and as a result, a large amount of water is passed out in urine.
Effects of Diuresis
- It leads to excretion of large amounts of urine.
- Diuresis leads to loss of weight.
- It also leads to emaciation.
- There is a high thirst for a lot of water.
Remedy
- Surgical operations should be performed on the patient.
- Drugs such as diuretics should be administered to get rid of excess water in the body.
Nephritis is a condition in Which the blood vessels in Bowman’s capsule (glomerular) become inflamed and porous as a result they cannot carry out the function of ultra-filtration completely which will result in the passage of most of the useful materials In the blood fluid with urine.
Effects of Nephritis.
- Inflammation of the Kidney
- presence of amino acids in urine
- weakness of the body
- fever
- pain.
Remedy.
- Use of dialysis- an artificial kidney can be adapted to take over the work of normal kidneys,
- Kidney transplant- The diseased kidney can be replaced with a healthy one.
- Use of antibiotics- Antibiotics can be used especially if the disease is caused by bacteria.
Kidney_stones: Kidney stones are caused by some diseased growths within the tubules. These diseased growths may narrow urine passage, thus reducing the free flow of urine. In most cases, the diseased growths may block the urine passage making the removal of urine extremely difficult.
Effects of Kidney Stones
- lt obstruct the passage of urine.
- Pain is experienced on passing out urine.
- Severe abdominal pain is experienced.
- It leads to high blood pressure, fever, chills, and blood in the urine.
Remedy
- Surgery called nephrectomy can be performed. This involves the opening up of the kidney to remove the stones.
- Patients should avoid excessive intake of calcium.
- A lot of water should be taken.
- There should be a reduction in protein intake.
Dropsy or Dropsy is a condition in which the cells of Bowman’s capsules are unable to absorb water from the blood in the tubules. As a result, a lot of water is retained in the blood or tissues which leads to the swelling of some parts of the body such as the face and ankles.
Effects of Oedema
- It leads to swelling in the face and ankles.
- It causes sluggishness.
- lt leads to abdominal pains.
- There is constant weakness or fatigue.
Remedy
- The patient should seek medical treatment by a specialist doctor.
- There should be a reduction in the intake of water.
- A kidney transplant can be performed if the condition is critical.






