Aquaculture SS3 Agricultural Science Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Aquaculture
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, pupils should be able to
- Define fish farming
- Explain some terms associated with fish farming
- State the importance of fish farming
- Highlight the conditions necessary for siting a fish pond
- Outline the classes of fish and give examples of each
- Discuss the processing and preservation of fish
AQUACULTURE
Fish farming (aquaculture) is the act of rearing selected species of fish under scientifically controlled conditions in enclosed bodies of water such as ponds, streams, rivers etc. where they feed, grow, breed and are harvested for consumption or sale.
Terms associated with fish farming
- Fingerlings – The newly hatched fish(es)
- Fisheries – This is the study of fish and fishes
- Fish – This refers to a particular species, regardless of the number or quantity
- Fishes– This refers to the different species of fish
- Pond– This is an artificial body of water where fish (es) can be reared
- Gears–These are equipment used in harvesting fish
- Fry- This refers to young fish (es) or baby fish(es)
- School– This is a group of fish (es)
- Hatchery–This refers to a unit where fish eggs are incubated and Hatched artificially into fish
- Aquarium –This is an artificial fish pond kept for aesthetic or entertainment purposes at home.
- Aquaculture–This refers to the study and production of fish, shrimps and other aquatic food organisms.
IMPORTANCE OF FISH FARMING
- To provides fish which serves as a source of food e.g. protein to man and livestock
- It provides a means of increasing the availability of protein to people at reduced cost
- It provides a means of recycling wastes e.g. animal dung from farms, factories and sewage disposal system
- Fish can be processed into fish by-products such as fish meal, fish oil, manure and skin
- It provides employment and income to many people
- A better use of land and water in our environment is also ensured through fish farming
- Fish farming is also useful in the area of research work and other educational purposes
CONDITIONS OF FACTORS NECESSARY FOR SITING A FISH POND
- Adequate water supply
- Soil in the area
- Vegetation of the area
- Topography of the area
- Availability of fast-growing fishes
- Availability of supplementary feedstuff.
CLASSIFICATION OF FISHES
Fishes can be classified into two main groups:
Classification based on fish habitat
- Freshwater fishes: These fishes live in freshwater i.e. the water does not contain salts. Examples of such freshwater include ponds, streams, rivers and lakes. Examples of fish in this group include tilapia, carp, perch, trout, mudfish etc.
- Saltwater fish: These fishes live in water containing salt such as lagoons, seas and oceans. Examples of saltwater fish include salmon, mackerel, shark, tilapia, rays, eels, etc.
Classification based on body structure
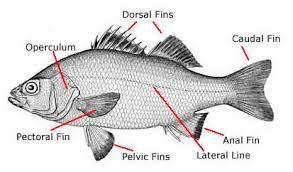
- Bony fishes: These fishes possess bony skeletons. Examples include tilapias, mudfish, carp, trout, catfish, salmon, perch, and herring. The majority of these fishes are found in freshwater.
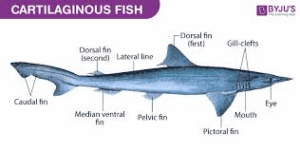
2. Cartilaginous fishes: These fishes possess soft bones composed of cartilage. The majority of these fishes are found in salt water and examples include sharks, dolphins, dogfish, and rays.
PROCESSING AND PRESERVATION OF FISH
Harvested fish is either consumed, sold or preserved for future use.
Fish processing involves the removal of scales, fins, gut and gills.
The remaining part is then cooked or fried for eating.
By-products of fish processing include
- fish meal
- fish scales
- cod liver oil
- fish skin.
Fish can be preserved for future use in any of the following ways:
- Salting: This is the application of salt to the fish. It prevents the growth of spoilage organisms
- Smoking: This is the drying of fish over naked fire. It reduces the moisture content and increases the taste and flavour of the fish
- Sun-drying: This involves the drying of fish using heat from the sun. in this process, fish can only be stored for a short time
- Freezing: This involves the use of cold storage like refrigerators and deep freezers to store fish over a very long time
- Canning: This involves the storage of processed and consumable fish in cans under special conditions for future consumption e.g. sardines.
EVALUATION:
- Define fish farming
- Explain some terms associated with fish farming
- State the importance of fish farming
- Highlight the conditions necessary for siting a fish pond
- Outline the classes of fish and give examples of each
- Discuss the processing and preservation of fish
CLASSWORK: As in evaluation
CONCLUSION: The teacher commends the students positively





















