Farm Accounts SS2 Agricultural Science Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Farm Accounts
Farm Accounts are statements of money paid out or received for goods and services used in a farming business.
TYPES OF FARM ACCOUNT
- Sales Account: Sales Account is also known as sales and receipt account. This shows data on farm produce, the quantity, date sold, to whom and at what price.
- Purchase Account: It is also known as purchased for use on the farm.
- Farm Valuation: This is the value of the farm at the beginning and end of production. At the beginning, it is called opening valuation while at the end, it is called closing valuation.
- Cash Analysis Account: It shows the details of the income and expenditure of a farm over a given period.
- Farm Income Statement: It comprises all the farm receipts (sales) and expenses that came out on the farm over some time as shown below;
INCOME STATEMENT OF AKANDE FARMS FOR OCTOBER, 1995
| EXPENSES | ₦ | RECEIPTS | ₦ |
| Feeds | 2000 | Egg | 5000 |
| Drugs | 400 | Culled layer | 3000 |
| Water | 100 | Manure | 200 |
| Labour | 500 | ||
| Fuel | 200 | ||
| Net income | 5000 | ||
| Total | 8,200 | 8,200 |
- Balance Sheet or Net Worth Statement: The balance sheet shows the capital or financial position of the farm at the end of the accounting period usually a year.
- Profit and Loss account: This is the type of account prepared at the end of the business period, usually a year. By a farmer to know whether his business is making a profit or loss.
In this account, all expenses and purchases are listed on the left-hand side i.e. debit side and all receipts on sales are recorded on the right hand i.e. credit side. Closing valuation is also put on the right while opening valuation is put on the left.
Importance Of Profit And Loss Account
- It helps to detect if the farm is making a profit or a loss.
- It helps to determine the overall performance of the farm at the end of the account period.
- It aids future planning of the farm for better results.
EXAMPLE:
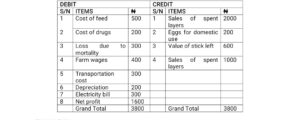
Prepare a profit and loss account for Segun Farms for the year which ended 31/12/17, using the following data;
Cost of feed N500
Cost of drugs N200
Sales of Eggs N2000
Eggs for domestic use N200
Loss due to mortality N300
Value of stick left N600
Farm wages N400
Sales of spent layers N1000
Transportation cost N300
Depreciation N200
Electricity bill N300
Net profit N1600
SOLUTION
SEGUN FARMS PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT AS OF 31ST DECEMBER, 2017
DEFINITION OF SOME ACCOUNTING TERMS
- Farm Asset: This is anything of value in the possession of a farm business, There are two types;
- Fixed Assets: These are assets which are not used up during production. Examples are; landed property, farm buildings, motor vehicles, tools and implements, incubators and milking machines.
- Current Assets: These are assets which are used up during the process of production eg water, feed, drugs, chemical, fertilizers, seeds and cash in the bank.
- Cost: these are expenses made during production. There are two types of fixed and variable cost
- Fixed Cost: This is the component of the total production cost which does not vary with the level of production e.g. cost of buildings, equipment, machinery, and farm structures (Silo, barn e.t.c)
- Variable Cost: This is the other component of the total cost which varies directly with the level of production e.g wages, salaries, cost of seeds, cost of fertilizer, cost of agrochemicals e.t.c
- Liabilities: This is the money owed to external persons or corporate bodies e.g. loans to banks. The two types are;
- Current or short-term liabilities: These are debts that must be paid back within one accounting year.
- Long-term liabilities: These are debts that cannot be paid within an accounting year.
- Net Capital, Net worth or owner equity: This is the total amount of money supplied by the owner of the farm business.
Asset Liability = Owner’s Equity or Capital.
- Liquidity: the ability of a farm business to meet its financial obligations as they fall due. It is the ease at which farm assets can be covered with cash.
- Solvency: This is the ability of the farm business to cover its liquidation of the asset. A business is solvent if the sale of its assets would be sufficient to pay off all debts.
- Appreciation: This is the increase in the value or worth of an asset as the asset is being used over time. Examples of assets that can be appreciated are; growing animals, cash crops, land etc.
- Depreciation: Depreciation refers to the loss or reduction in the value or worth of an asset as the asset is being used over time.
- Salvage Value: This is the amount at which an asset is sold off when it is no longer economical to keep, or when the cost of maintenance is too high.
- Useful life Span: This means the number of years a piece of farm equipment can effectively serve the farmer.
ASSIGNMENT
- In profit and loss account, opening valuation is put on the _____ A. credit side B. debit side C. and side D. all sides
- Ability of the farm to meet its financial commitment as the falls due is _____ A. solvency B. liquidity C. depreciation D. appreciation
- The amount at which an asset is sold off when the cost of maintaining it is high is called ____ A. useful life B. lifespan C. salvage value D. asset
- Day-to-day activities on the farm are recorded in _____ A. register B. diary C. payroll D. inventory
- Farm assets are recorded in _____ A.diary B. register C. inventory D. labour






















