Lenses SS2 Physics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Lenses
Lenses are used as magnifying glasses. They are also used in microscopes, telescopes, cameras and projectors. The human eye has a natural lens which enables people to see clearly. There are two types of lenses: Converging and Diverging lenses.
The converging lens brings light rays together while the diverging lens spreads light rays apart. A converging (convex) lens bulges at the centre while a diverging lens gets thinner at the centre.
TERMS
Terms which are commonly used in lenses include the principal axis of a lens, the principal focus of a lens, the optical centre of a lens, and the focal length of a lens.
- The principal axis of a lens is the line joining the centre of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens, and passing through the middle of the lens.
- The principal focus of a lens is the point on the principal axis to which all rays parallel and close to the axis converge or diverge, after refraction of the lens. The principal focus of a converging lens is real, while that of a diverging lens is virtual.
- The optical centre of the lens is defined as the centre of the lens which is a point on the principal axis of the lens. Rays of light which pass through the optical centre are undeviated.
- The focal length of a lens is the distance between the optical centre and the principal focus of the lens.
FORMATION OF IMAGES IN LENSES
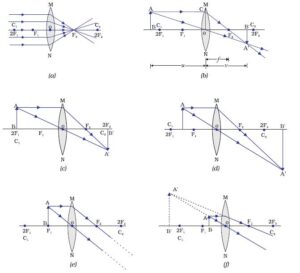
CONVERGING LENS
To produce the image of an object by a converging lens, two major rays are required:
- A ray from the top of the object incident on the middle, c, of the lens and passes through the lens undefeated.
- A ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis, incident on the lens, and refracted through the principal focus, F. At the point where these two rays interact, the image of the object is formed.
OBJECT AT INFINITY
When an object is very far from the lens i.e. at infinity, the image is real, inverted and formed at the focus of the object beyond 2f1.
OBJECT BEYOND 2F1
When an object is very far from the les i.e. at infinity, the image is real, inverted and formed at the focus of the object beyond 2f1.
OBJECT BEYOND 2F1
When an object is placed beyond 2F1, the image of the object is formed between F and 2F and is real, inverted and smaller than the object (diminished).
POWER OF A LENS
The power of a lens is the reciprocal of the focal length of a lens in metres.
P = 1/f
THE SIMPLE MICROSCOPE OR MAGNIFYING GLASS
A complex lens gives an enlarged upright virtual image of an object placed inside the principal focus. This constitutes a simple microscope. It is used for reading and studying biological specimens.
ASSIGNMENT
- The screen of a pinhole camera is a square of side 0.16m and it is 0.15m behind the pinhole. The camera is placed 11m from a flagstaff and positioned so that the image of the flagstaff is formed centrally on the screen. The image occupies three-quarters of the height of the screen. What is the height of the flagstaff?
- A converging lens of focal length 15cm forms a virtual image at a point 10cm from the lens. Calculate the distance of the object from the lens