Public Finance SS2 Economics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Public Finance
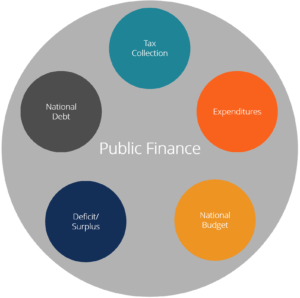
Public finance can be defined as an aspect of economics which deals with the financial activities related to Income, Expenditure and National debt operations, with their overall effects on the economy. That is, it is the management and control of government income and expenditure to achieve the government’s policy objectives. It involves a detailed analysis of the various sources from which the government derives its income (revenue), the items on which the government spends its money and the impact of such government expenditure on different aspects of the economy.
OBJECTIVES OF PUBLIC FINANCE
- It performs equitable distribution of resources among individuals, tiers of government and the various sectors of the economy.
- It is used to achieve and maintain a favourable balance of payments and economic development.
- It provides a general parameter for monitoring the economy in terms of growth and stability.
- It is used to achieve the economic objectives of the government.
- It is used to ensure good fiscal policy for the regulation of the economy.
- It is used to generate employment avenues for the people.
- It is to ensure the satisfaction of the needs of the people through the provision of funds for transfer payments e.g. pension fund, unemployment benefits, subsidies etc.
FISCAL POLICY
This may be defined as a government plan of action concerning the raising of revenue through taxation and other means and deciding the pattern of expenditure to be applied.
Fiscal policy therefore involves the use of government income and expenditure instruments to regulate the economy to achieve some set economic objectives
The Economic Objectives of the Government on Fiscal Policy include:
- Maintenance of stable prices/control of inflation and deflation.
- Equitable distribution of wealth.
- Efficient allocation of resources.
- Provision of full employment.
- Stability in the exchange rate of the national currency.
- Maintenance of favourable balance of payments.
GOVERNMENT REVENUE
Government Revenue is the total income that is accrued to all levels of administration or government from various sources.
Classification Of Public Revenue
Government revenue can be classified as:
- Recurrent Revenue: This is the total amount of revenue collected by the government of a country on a regular or yearly basis e.g. taxation, fees, licenses, fines etc.
- Capital Revenue: This is revenue from irregular or extraordinary sources. They are sources of revenue used for meeting expenditures on heavy capital projects e.g. grants or loans collected by the government to build a project e.g. railway line.
Sources Of Government Revenue
The main sources of government revenue are
- Taxes: are major forms of source of revenue to governments all over the world. These taxes may be direct or indirect.
- Royalties: This is the money paid by companies engaged in mining activities to the government for rights to explore and exploit mineral resource deposits
- Earning (income) from government investments e.g. interest, rent, dividends, profits from government-owned business property.
- Grants and aid from individuals and institutions at home and from foreign governments and international organizations.
- Borrowing: This could be internal or external borrowing e.g sale of government securities or loans from the African Development Bank, IMF, World Bank, Pars Club etc
Fees, licenses and charges, fines etc eg vehicle license fees, liquor license fees, firearms license fees, international passport fees, court fines, Road Safety Commission fines etc
- Other sources e.g. Tolls, rates etc.
GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE
This is the total expenses incurred by public authorities at all levels of administration in the country. This includes money spent by the government on building roads, bridges, schools, hospitals, corporations and other permanent investments.
Classification Of Public Expenditure
Government expenditure can be classified as:
- Recurrent Expenditure: These are expenditures incurred in the running of the day-to-day activities of the government. They are expenses that reoccur within a fiscal year i.e. items/expenses that last for less than a year e.g. wages, salaries, stationery, fuel for official cars, cost of maintaining roads, repairs expenses on dams etc.
- Capital Expenditure: These are expenditures (investments) on projects that last for more than one year. They are used to acquire permanent assets e.g. construction of roads, bridges, government buildings, purchase of cars etc. In most cases, recurrent expenditure is spent on maintaining capital projects.
Objectives Of Government Expenditure
The main items of government expenditure are meant to achieve the following objectives:
- Defense or National Security: The government provides for the Army, Air Force, Navy and the Police to maintain law and order and defend the country from external aggression.
- General Administration: The government spends money on maintaining the Civil Service and the various officers of the government in the ministries, agencies, corporations, parastatals and departments
- Providing Social Amenities: The government spends money to provide educational facilities, supply of pipe-borne water, roads, bridges, ports, telecommunication, power and electricity, etc.
- Servicing National Debt: Government spend money on the repayment of the principal and interest of both internal and external debts, including payments of pension
- Direct Productive Service: Governments sometimes participate directly by organizing the production of some commodities to promote economic activities and services.
Reasons For Increase In Government Expenditure
There has been an astronomical increase in the magnitude of government expenditure. Some of the reasons for this include:
- Population Explosion: Increase in population leading to higher administration costs
- Inflation: The effect of inflation (a general increase in price level) on the cost of projects undertaken by the government.
- Devaluation: The effect of devaluation (depreciation) of the Naira on the largely import-dependent economy of Nigeria leads to high expenditure.
- Administrative Cost: The increasing cost of maintaining democratic institutions and a large number of political structures i.e. states, local governments and their officials.
- Social Amenities: Greater demand for social and economic infrastructures and the cost of maintaining existing ones.
- Economic Development: The economic development programme of the government requires a lot of capital outlay to import the needed equipment/machines.
- Rise in National Debts: The cost of servicing the country’s huge stock of internal and external debt has kept increasing because of interest capitalization
- Bribery and Corruption: The high prevalence of corruption and over-invoicing of the cost of projects by government officials and politicians.
- Defense / Security Expenses: A rise in defence also increases government expenditure.
- Unemployment: Attempts by the government to combat unemployment also lead to an increase in government expenditure
Poverty- efforts by the government to alleviate poverty often lead to high expenditure.
Effects Of Public Expenditure
- Some government expenditures help to redistribute the income of the people.
- Government expenditure in industrial investment helps to generate employment for people.
- Government expenditure helps to allocate certain resources in certain areas to enhance the even distribution of resources.
- Government expenditure helps to stabilize the prices of goods and services.
- Government expenditure in industries helps to create increased productivity and income for individuals with a rise in their purchasing power.
ASSIGNMENT
- Which of the following is not an item of capital expenditure
(a) Building of dams (b) Supply of electricity (c) Payment of interest on loans (d) Building of harbours.
- Public expenditure on education and health is known as the expenditure of
(a) general services (b) social services (c) commercial services (d) economic services.
- Which of the following is an item of Recurrent Expenditure
(a) Construction of Highways (b) Building of Dams (c) Payment of Salaries and WSages (d) Building of a new University.
- Which of the following items cannot be classified as Essential Government Expenditure
(a) Construction of Roads (b) Servicing of External Debts
(c) Maintenance of public Hospitals (d) Importation of Luxury Consumer Goods.
- Which policy is used to adjust government revenue and expenditure to produce a desirable effect on the economy
(a) monetary (b) business (c) physical (d) fiscal.