Cost Concept SS2 Economics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Cost Concept
MEANING OF COST OF PRODUCTION
Cost of production can be defined as the sum of the total of all the payments to the factors of production used in the production of goods and services.
For goods and services to be produced, all the four factors of production, which are land, capital, labour and entrepreneur, must work together.
ECONOMIST’S VIEW OF COST
Economists view cost as opportunity cost. He is not concerned about the real amount of money spent on a particular item but the value of the sacrificed alternative. For example, if an individual bought a shoe instead of a handset. The opportunity cost is the handset forgone.
ACCOUNTANT’S VIEW OF COST
To an accountant, cost is the total amount of money spent to acquire a product.
TYPES OF COST
- Total Cost (TC): Total cost may be defined as the total sum of fixed and variable costs incurred by an enterprise in the production of a particular commodity.
Total cost = Fixed cost + variable cost or Average cost x Quantity.
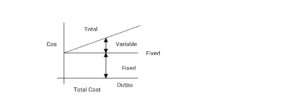
- Fixed Cost (FC): Fixed cost, also called overhead cost or unavoidable cost, is defined as the cost that remains constant in the short run no matter the level of output. E.g. money spent on rent, etc.
FC = Total Cost – Variable or TFC = AFC x Q

- Variable Cost (COST): Variable cost, also called direct cost, is defined as the cost of production which varies or changes directly with the level of output. E.g. cost of raw materials, labour, etc. VC = TC – FC

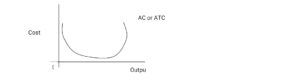
4. Average Cost (AC) OR Average Total Cost (ATC): Average cost is defined as cost per unit of output.
Average cost is the total cost of producing a given output divided by the number of units of output.
AC = Total cost ÷ Total Output OR
ATC = AFC + AVC
- Average Variable Cost: The average variable cost is the cost per unit of variable cost of output.
AVC = TVC ÷ TQ = ATC – AFC
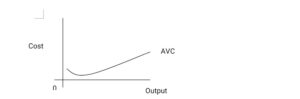
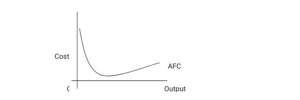
- Average Fixed Cost (AFC): This is the fixed cost per unit of output.
AFC = Total fixed cost
Quantity
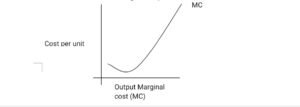
- Marginal Cost (MC): It is referred to as incremental cost. Marginal cost is the addition to the total cost needed to produce a unit increase in output.
Marginal cost does not depend on fixed cost but on variable cost, because fixed cost does not vary with the level of output.
Marginal Cost = Change in TC
Change in output