Channels Of Distribution SS1 Economics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Channels Of Distribution
Channels of distribution are also known as distributive trade or chain of distribution. It refers to the various stages or channels through which finished goods are moved from the manufacturers/producers to the final consumers.
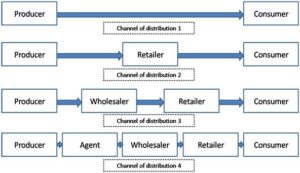
That is, it is the process of getting goods from the producer to the final consumers. There are various channels through which goods get to the final consumer commonly called channels of distribution. The common channel through which the consumer gets the goods is represented as:
Manufacturer /Producer > Wholesaler > Retailer > Final consumer
PROCESS OF DISTRIBUTION
Process of Distribution- involves all human and physical means which aid the smooth transfer of goods from the manufacturers to the final consumers. The process of distribution involves:
- Middlemen- the middlemen or agents are human elements involved in the distribution of goods from the producers to the final consumers, eg wholesaler and retailer
- Transportation- is the medium through which the finished goods are moved by air, land or water from the manufacturers to the final consumers
- Advertisement- is the process of creating awareness in the mind of the public about the existence of a product.
- Warehousing- a process through which the goods produced are stored until they are needed.
THE WHOLESALER
A wholesaler may be defined as a trader who buys goods in large quantities from the producer and sells them in small quantities to the retailer. The wholesaler is an essential and desirable element in the channel of distribution and production. He is sometimes called a middleman because he is in between the producer and the retailer.
FUNCTIONS OF WHOLESALER TO THE PRODUCER
- Bulk breaking: This is one of the most essential functions of the wholesaler as he can satisfy the needs of purchasing in large quantities from the producer.
- The wholesaler finances the producer by making prompt or advance payment for goods.
- He also finances the retailer by giving credit facilities to them.
- He helps to make the prices of goods stable especially where production is irregular.
- He provides warehousing or storage facilities for goods bought.
- He gives vital information about the market situation to the producer.
- He completes the manufacturing of some goods by doing the packaging and branding.
- Wholesalers help to create markets for producers and themselves through large-scale advertising use of sales representatives etc.
FUNCTIONS OF WHOLESALER TO THE RETAILER
- He enables the retailer to stock a variety of goods
- He provides the retailer with credit facilities
- He advises the retailer based on his expert knowledge of the product
- He provides a link between the producer and the retailer
- He helps to transport goods to the retailer’s shop
THE RETAILER
A retailer may be defined as a trader who buys goods in small quantities from the wholesaler or directly from the manufacturer and sells them in units to the final consumer.
He is essentially in the channel of distribution because he is the last link to the consumer, so he is also a middleman.
Retail trade can be broadly classified into two types namely; large-scale retail trade and large-scale retaittrSmSmall-scale retail retail trade cocomprisesiosk, market or stallholder retailing, street or roadside retailing, cycle boys, mobile shops retailing, itinerant or hawking retailing etc.
Large-scale retailing can be in the form of department stores, multiple bishops supermarket all-order businesses, hypermarkets, and retail co-operative societies.
FUNCTION OF THE RETAILER
- The retailer stocks a variety of goods to satisfy the taste of the consumer.
- He brings goods to the consumer thus saving the consumer the inconvenience of going far.
- He assists the producer and wholesaler in promoting lesser-known goods
- He advises the consumer and wholesaler on how to use certain products and about new developments in the market
- He provides after-sales services, especially for technical products like computers, televisions etc.
- He finances the consumer by selling at time on credit.
- He completes the distribution chain by making goods available to the consumer; thus completing the production
- He provides market information to buyers and sellers
- He advertises the goods through fascinating window displays
THE MIDDLEMEN
The middlemen are the wholesalers and the retailers who are in between the producers and the consumers. They specialize in performing activities relating to the purchase and sale of goods in the process of their flow from the manufacturers to the final consumers. The presence of the middlemen in distributive trade cannot be overlooked as they play a vital role in linking the producers with the ultimate consumers for effective trading activities.
REASONS THAT MAY WARRANT BY-PASSING THE MIDDLEMEN
- Some manufacturers by-pass the wholesaler and sell to retailers for the following reasons
- Where perishable goods are involved
- The establishment of warehouses by the producer
- Indiscriminate increase in prices of goods and services
- When good are branded
- When consumers combined to buy in bulk
- When manufacturer open their retail stores
- Their creation of artificial scarcity
- Where the goods produced are highly technical or made to individual specifications
PROBLEMS OF DISTRIBUTING AND MARKETING GOODS IN WEST AFRICA
- Poor and inadequate transportation facilities
- Inadequate storage facilities
- Too many middlemen
- Administrative bottleneck in the collection and handling of goods
- Inadequate credit facilities
- The imperfect nature of the market due to inadequate information
- The tendency to hoard goods in anticipation of higher prices
- Inadequate infrastructural facilities
- Inadequate dissemination of information
EFFICIENT WAYS OF DISTRIBUTING AND MARKETING GOODS IN WEST AFRICA
- Good and efficient transportation network
- Provision of good storage facility
- Formation of consumer and wholesale co-operative societies
- Goods rationing in case of essential commodities.
- Provision of credit facilities to wholesale and retailers
- Providing adequate information on the market situation
- There should be legal action against hoarders
- Establishment of more marketplaces
- Construction of a good road network
- Improvement in communication system
ROLES OF GOVERNMENT IN DISTRIBUTIVE TRADE
The government at whatever level has a major role to play in the distribution of goods through the establishment of distributive agencies such as:
- Establishment of the Nigeria National Supply Company (NNSC) Ltd
- Marketing Board
- The River Basin Authorities to encourage large production and distribution of agricultural produce
- Provision of a good transport system
- Provision of better storage facilities
- Government agencies help to stabilize prices to check inflation
- Government agencies help to prevent artificial scarcity of goods
- Government agencies also play the role of price control
- Establishment of communication system
ASSIGNMENT
- Which of the following functions do retailers perform in an economy?
(a) production (b) exchange (c) hoarding (d) distribution
- One of the arguments against the presence of middlemen in the distribution chain is that they
(a) can be found always here (b) Helps in keeping prices stable © causes an increase in the prices of commodities (d) are commissioned agents
- One of the greatest demerits of the middlemen in Nigeria is that they
(a) sell in small units only
(b) increase the prices of goods and services at will (c) store goods in warehouses that are spacious enough (d) do not advertise their goods
- Distribution involves the
(a) transfer of goods and services from wholesaler to consumer (b) transfer of goods and services from production centre to consumers (c) movement of goods and services by middlemen to centres (d) transfer of goods and services from one market to another
- A major function of middlemen in Nigeria is the distribution
(a) commodities at all consumers regardless of income (b) commodities to consuming centres (c) wealth to all (d) economic facilities to all