Database Management System II SS1 Data Processing Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Database Management System II
CREATE FIELDS WITH DATA TYPES
Fields are assigned field names relevant to the information they keep. Field names are assigned data types which determine the kind of data they accept as input. For example in the MS Access table above, the Surname is alphabetic, and the fields will not accept numeric (numbers) inputs 10 or 500 as a surname. To set the data type for the field in MS Access, follow the steps below;
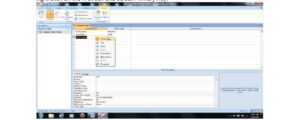
i. After creating the table in design view under the field name tab, then type the field name and under the data type tab next to the field name, click the drop-down menu and select Auto Number as shown below.
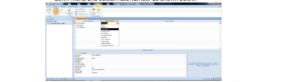
For example, using the above picture screen, the field name ID Number will be assigned a Number data type since the ID Numbers will be numeric. In the same way, the TEXT data type will be assigned to Surname and First name.
UNIQUE IDENTIFIER
A table contains a unique identifier i.e. a KEY. In MS Access, a default primary key is usually specified for the first field. To set another field of your choice as the primary key, right-click on the first cell and select Primary Key.
Note: The symbol of a key should appear beside the field, after setting that field as a unique identifier. If it does not appear repeat previous steps.
CREATING A DATABASE
Generally, creating a database using any DBMS entails the following basic steps:
- Define the Database Structure
- The database structure specifies the type of database organization that should be used. If the relational form is selected, the database structure will include RDBMS, the structure of a table, the number of rows, the number of columns, the key, and the relationship of the database etc.
SPECIFY FIELD TYPE
When a database is being created, all fields are set to accept a particular type of input by specifying a field type. A field type is also known as a Data type. The essence of a data type is to prevent a wrong input from being stored in a database (i.e. database integrity). Usually, the name of a data type varies with DBMS but portrays a general meaning. These include;
i. Alphanumeric/ text field: Fields that accept both numbers and text e.g. ASP2548.
ii. Numeric Fields: Fields that accept numbers in two forms: Real numbers i.e. decimal numbers e.g. 8.15, 9.1 and integers’ i.e. whole numbers e.g. 125, 80 etc.
iii. Date Fields: They store data in date format e.g. 11-04-2009
iv. Boolean fields: The data accepted by these fields are either Yes/No or True/False.
v. Memo: Long text. Use for long pieces of text. Such as notes and long descriptions. Can store up to 64,000 characters.
vi. Currency: Use for currency.
vii. AutoNumber: Unique sequential numbers or random numbers are automatically inserted when you create a record. Use to create a primary key.
viii. Hyperlink: Use to store hyperlinks
ix. Attachment: used to store attachments e.g. files, images etc.
x. OLE Object: Use to attach an OLE object such as a Word document, Spreadsheet, or PowerPoint Presentation
INPUT DATA
After the field names and their data types have been specified, the records are stored in the database by specifying the appropriate input. In MS Access, to input data:
- Double-click on the Student Table at the left-hand pane of MS Access windows
- Enter the data beneath the field names and click on the next cell to populate the data.
To keep the database updated, data inputted into the database must be saved regularly. Keyboard command CTRL + S is used. Alternatively, you click on the Office button and save.
BASIC OPERATION
The basic operations to be considered are:
- Searching
- Sorting
- Modifying
- Generate report
- Searching
i. On the Tools Menu, click Options
ii. Click the Edit/Find tab
iii. Under Default find/replace behave, do one of the following:
– Select Fast Search to search the current field and match the whole field.
– Select General search to search all fields and match any part of the field.
– Select Start of Field Search to search the current field and match the beginning characters of the field.
DBMS have certain commands for saving a database. For example in MS Access, select the save option on the MS Access window to save.
- Sorting
a) To sort records in form view or datasheet view, follow these steps:
i. Start MS Access, and then open the database that you are working with.
ii. Open the table or the form whose data you want to view.
iii. Click the field that you want to use for sorting records. To sort records in the sub-form, click the field that you want to sort. To sort records in a sub-datasheet, display the sub-datasheet by clicking the expand indicator, and then click the field that you want to sort.
iv. On the records menu, point to sort, and then click Sort Ascending or Sort Descending.
NOTE: In a form, you can only sort on only one field at a time.
b) Sorting with sub-datasheet
In the datasheet view, when you sort the sub-datasheet for one record, MS Access sorts all the sub-datasheets at that level. In a datasheet or sub-datasheet, you can select two or more adjacent columns at the same time, and then sort them. Access sorts records starting with the leftmost selected column. When you save the form or datasheet, Access saves the sort order.
c) Sorting Records on a Report
i. Start MS Access, and then open the database that you are working with.
ii. Open the report in Design View.
iii. ON the View menu, click Sorting and Grouping to display the sorting and Grouping dialogue box.
iv. In the first row of the Field/Expression column, select a field name or type an expression.
NOTE: When you fill in the Field/Expression column, MS Access sets the sort order to Ascending.
You can sort up to 10 fields or expressions in a report. To sort your report on more than one field, add another field or expression to the Field/Expression column. The field or expression in the first row is the first sorting level. The second row is the second sorting level, and so on.
- Modifying Data
How to add or edit Data in a Datasheet (Table or Query) or a Form
Open a table or a query in the datasheet. View or a form in Form View.
Do one of the following:
i. In MS Office Access 2003 or in earlier versions of Access, to add a new record, point to Go on the Edit menu, and then click New Record. Type the data, and then press TAB to go to the next field. At the end of the record, press TAB to go to the next record.
ii. In MS Office Access 2007, to add a new record, click the Home tab, and then click New in the Records group.
NOTE:
– To edit data within a field, click on the field that you want to edit, and then type the data.
– To replace the entire value, move the mouse pointer to the leftmost part of the field until the pointer changes into the plus pointer, and then click. Type the data.
NOTE: To correct a typing mistake, press BACKSPACE. To cancel your changes both in the current field and the entire record, press ESC.