Heat Energy SS1 Physics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Heat Energy
Concept of Heat
Heat is a concept of physics that deals with the study of the relative motion of a fluid (liquid and gas) from one body to another. It is a form of energy that can be transferred from one body due to temperature differences.
Temperature
Temperature is the degree of hotness and coldness of a body or an object. It is a scalar quantity, measured in Kelvin. Heat and Temperature are similar but not the same
Differences between Heat and Temperature
Heat is a measure of the total internal energy of a body while temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of the body.
Heat takes place due to temperature difference while temperature occurs due to slight changes of substance.
Heat is measured in joules while temperature is measured in Kelvin / Celsius.
Effects of Heat
When heat is applied to a body the following effect may occur:
- Expansion: when heat is applied, volumes increase while density decreases.
- Change in temperature: When heat is added to a body, the temperature increases
- Change of state: melting, freezing, condensation, evaporation etc.
- Thermion Emission: The addition of heat on metal may result in the emission of electrons from the surface of the metal
- Photoelectric Emission: The emission of electrons when sufficient light of high frequency is illuminated on a metal surface e.g. zinc plate.
Thermometers and Their Thermometric Substance
Thermometric substances are substances which change in proportion to temperature.
| SN | THERMOMETER | THEMOMETEOCAL SUBSTANCE | PHYSICAL PROPERTIES |
| 1 | Liquid in glass | Mercury or alcohol | Change in volume with temperature |
| 2 | Constant volume glass thermometer | Gas | Change in pressure with temperature |
| 3 | Thermometric thermometer | Two different metals (Iron and Copper) | Change in potential difference due to temperature difference |
| 4 | Resistant thermometer | Resistant wire | Change in resistance with temperature |
| 5 | Bimetallic thermometer | Two dissimilar metals (brass and iron) | Differential expansion of two metals of the bimetallic stripes |
Advantages Of Mercury As A Thermometric Substance
i. Mercury does not wet glass.
ii. Mercury responds quickly to a slight change in temperature.
iii. The liquid does not vaporize easily.
iv. Mercury is opaque Hence, it can be seen easily.
v. It has a regular or uniform expansion.
Disadvantages
- Mercury is expensive
- Mercury can not be used to measure very low temperature because of its freezing point – 39˚C
Advantages Of Alcohol As A Thermometric Substance
- Alcohol is less expensive than mercury.
- It has a larger expansion on heating than mercury (it expands 6 times more than mercury).
- It can be used to measure very low temperatures.
Disadvantages
i. It is not opaque and so must be colored.
ii. It vaporizes easily.
iii. It is wet glass.
iv. It has an irregular expansion.
v. It has a low boiling point of 78˚C.
Constant Volume Gas Thermometer
- It gives a more accurate measurement of temperature than any other thermometer.
- It is very sensitive and can measure a wider range of temperature.
Disadvantages
- It is very expensive and so requires handling with special care.
- It is very cumbersome.
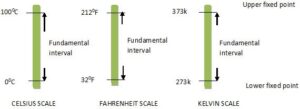
FIXED POINT OF THERMOMETER
Fixed temperature points are two reference temperatures (usually upper and lower fix points) chosen when preparing a scale for reading temperatures.
Upper Fixed Point: the temperature of steam from pure water at the normal atmospheric pressure.
Lower Fixed Point: is the temperature of the mixture of pure ice and water at normal pressure.
Fundamental Intervals: the interval between the upper and lower fixed points.
REASON WHY WATER IS NOT USED AS A THERMOMETRIC
- Water wet glass
- They are colorless
- It does not expand uniformly
- It has a small range of expansion (0˚C to 100˚C)
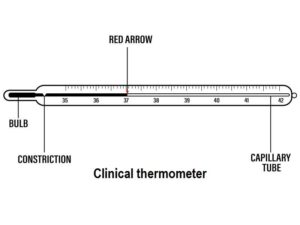
CLINICAL THERMOMETER
It is used for measuring the temperature of the human body. The body temperature ranges from (35˚C to 45˚C). It is not advisable to sterilize a clinical thermometer in boiling water because a short range of 35˚C to 43˚C shall result to cracking or breaking of the thermometer due to excessive expansion of the mercury.
Expansion of Solid, Effect and Applications of Expansion
- Effect and Application of Thermal Expansion of Solid
When hot water is poured into a glass tumbler, it might crack due to the uneven expansion of the inner wall of the tumbler.
The cracking noise of the zinc roof during the day and night.
Thermal expansion of solid is used in the construction of bridges in which one side is fixed and the other is placed on rollers to allow for expansion.
The stopper of a bottle can be removed due to the expansion of the glass.
In the construction of concrete pavement, little spaces are left within the concrete to allow for expansion. Gaps are left in the construction of railway tracks to give room for expansion.
Bimetallic stripes are used in thermostats for controlling or regulating the flow of electric current.
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermal Expansion of Solid
Advantages
i. Fire alarm e.g. electric bell.
ii. The fittings of wheels in rims.
iii. Bimetallic thermometer.
iv. Red hot rivet in shipbuilding.
v. Bimetallic stripes used in thermometers e.g. electric cookers etc
- Disadvantages
i. Cracking of drinking glass when hot liquid poured inside.
ii. If the balance wheel of a watch expands the time will be fast and if the balance wheel of a watch contrasts the time will be slow.
iii. Expansion of metal of concrete bridges which can lead to eventual after a long period.
iv. Sagging of overhead wire due to contraction in the winter season
v. Expansion of railway tracks thereby forming distant railway tracks.
vi. Bursting of water metal pipes.
ASSIGNMENT
- Gaps are left in the construction of railway tracks to give room for. a. contraction B. evaporation C. expansion D. vaporization
- When hot water is poured into a glass tumbler, it might crack due to the inner walls of the tumbler a. even expansion B. uneven expansion C. uneven contraction D. even contraction
- The stopper of a bottle can be removed due to the of the glass a. contraction B. expansion C. evaporation D. none of the above
- The following are advantages of thermal expansion of solids except a. bimetallic thermometer B. fire alarm C. sagging of overhead wire D. fitting of wheels in rims
- If heat is removed from solids they a. contract B. evaporate C. expand D. none of the above
- Mention four effects of the thermal expansion of a solid.
- Mention four of the advantages and disadvantages of the thermal expansion of a solid.