The Nigerian Climate SS1 Geography Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: The Nigerian Climate
The climate model is the average weather condition of the atmosphere over a long period of it 30-35 years.
FACTORS AFFECTING CLIMATE
- Latitude
- Altitude
- Distance from the sea
- Ocean currents etc.
ELEMENTS OF CLIMATE
- Temperature
- Rainfall
- Wind
- Relative humidity
- Pressure
- Cloud cover
- Sunshine
- Temperature: It is the degree of hotness and coldness of a place. temperature turnover in Nigeria is not uniform and has the following characteristics:
i. It varies from place to place: Temperature is low in the south with an average temp. of about 24°C because of the cooling effects of the Atlantic Ocean, while it is high in the north due to the effects of the Sahara desert or distance from the sea.
ii. It varies with altitude(height): places in Nigeria with high altitudes like Jos plateau, obudu etc have lower temperatures (20oC) while the surrounding lowlands experience high temperatures (of over 27oC).
iii. It varies with seasons: During rainy seasons, temperatures are usually higher in the north but lower in the south during the dry season due to the effects of harmattan.
iv. Variation in annual range: The annual range of temperature in the south varies from 2-3oC while that of the north is about 9oC.
- Wind: Wind is defined as air in motion. Nigeria is characterized by four types of wind which are:
i. The Tropical Maritime Air Mass (southwest trade wind): This wind comes from the Atlantic Ocean and brings about the rainy season to southern parts of Nigeria, especially around Warri and Port-Harcourt with twelve months of continuous rainfall. The Rainy season in the south starts from March- October, with a short dry season in August called AUGUST BREAK.
ii. Tropical Continental Air Mass (northeast trade wind): This trade wind is responsible for the dry season in northern parts of Nigeria. It comes from the Sahara desert. It is cold, dusty and dry hence, it does not bring rain but it brings a very cold, dusty and dry weather called harmattan. It starts in November and ends around February.
iii. Equatorial Easterlies: This wind blows around the equator from the east. It has some influence on the N.E AND S.W trade winds when they meet.
iv. Land and sea breeze: these local winds are restricted to the coast of Lagos, Warri, Port Harcourt, etc. These are local winds which blow alternately between land and sea daily
SEASON
There are two types of seasons in Nigeria. The two seasons are the wet and the dry season. During the dry season, the tropical continental air mass and the southwesterly wind influence the whole of Nigeria.
During the dry season, most parts of the country are influenced by the tropical continental air mass.
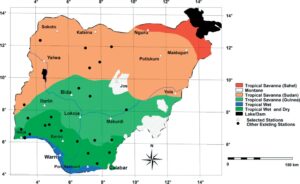
- Rainfall:- Rainfall in Nigeria is unevenly distributed. It generally increases from the coast inland. Along the coast, rain falls for about 8 to 12 months of the year. Further inland, the period of rainfall decreases to less than six months. The shortest periods of rainfall are to the northwest and northeast, where rain falls for less than four months of the year.

The mean annual rainfall varies from about 2000mm along the coast to less than 600mm in the northern part of the country.
4. Insolation and Sunshine: Insolation is generally high throughout the year in Nigeria. Relatively less amount of insolation is received in the south where cloud cover is thicker than in the north where clouds are less. The highest amount of insolation is received in the north. Sunshine hours are less in the rainy season than in the dry season.
- Relative Humidity: Relative Humidity decreases towards the North, Humidity is higher in the South than in the North. Humidity is also higher in the rainy season than in the dry season.






















