Units Of Measurements And Electrical Continuity Testing SS1 Physics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Units Of Measurements And Electrical Continuity Testing
MEASUREMENT OF MASS, WEIGHT, LENGTH & TIME
TECHNIQUES AND MEASUREMENT
Measurement is an important aspect of physics and other sciences. No fact in science is accepted, and no law is established, unless it can be exactly measured and quantified. As physics is based on exact measurements, every such measurement requires two things; first a number or quantity, and secondly a unit, e.g. 20 metres as the length of a table tennis board.
- MEASUREMENT OF LENGTH
THE METRE RULE: The metre rule is often used to measure distances of a few centimetres to some metres, for example, the dimensions of a table or room. When longer distances are involved, the ape rule can be used. 0.1 cm or 1mm is the smallest graduation on a metre rule.
 Callipers:
Callipers:
Callipers are used to measure distances on solid objects where an ordinary metre rule cannot be applied directly. They are made of hinged steel jaws which are closed (in the case of external callipers) until they touch the desired part of the object being measured. The distance between the jaws is then measured on a graduated scale such as the metre rule.
iii. The Vernier Callipers:
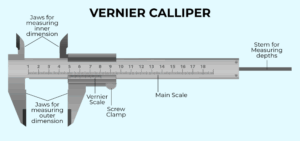
These can measure length more accurately than the metre rule. To measure small lengths, to the nearest 0.1mm, e.g. the thickness of a metre rule, the internal and external diameters of a tube, or the diameter of a rod, we use the vernier callipers. The instrument has two sets of jaws and two scales, the main and the vernier scales
The Micrometer Screw Gauge:
This instrument measures even smaller lengths (e.g. diameter of a wire) than the vernier callipers. It has a higher reading accuracy and can read up to 0.01mm or 0.001cm. It can be used to measure the thickness of a piece of paper or the diameter of a small ball (e.g. pendulum bob).

-
MEASUREMENT OF TIME
The time interval between two events is the difference between the times when the event occurred when the time interval is of the order of minutes or hours, clocks and watches can be used. These are the instruments which indicate the time of the day. For shorter time intervals of the order of seconds, stop clocks or stopwatches are used
MEASUREMENT OF MASS
The mass of a body is a measure of the quantity of matter it contains. Mass is usually measured by comparing it with standard masses, using a balance.
There are various types e.g. beam or chemical balance, lever balance, a dial spring, direct reading balance etc
WEIGHT: of a body is the force acting on the body due to the earth’s gravitational pull. One instrument used for measuring weight is the spring balance. Weight is measured in Newtons.
Differences Between Mass and Weight
| SN | Mass | Weight |
| 1 | It is the quantity of matter present in a body | It occurs due to the force of gravity açting upon an object |
| 2 | Mass is constant | Weight varies |
| 3 | Mass is a scalar quantity | Weight is a vector quantity |
| 4 | The unit of mass is kg | The unit of weight is Newton |
| 5 | Mass is measured by chemical or beam balance | Weight is measured withà spring balance |
| 6 | The principles of the moment are applied to obtain the mass | The instrument for measuring weight obeys the Hooke’s law |
Relationship Between mass & weight
W=mg
Where, W = weight(N) m=mass(kg) g= acceleration due to gravity(m/s2)
-
MEASUREMENT OF VOLUME
GRADUATED CYLINDER: A graduated cylinder can be used for the measurement of volumes of liquids. It is accurate to the nearest 1cm3. It can also be used in measuring the volume of irregularly shaped objects e.g. stone, with the aid of the displacement or eureka can.
HOW TO READ A VERNIER CALLIPER
In reading a vernier calliper, the whole number (digit before the decimal point) and the first digit after the decimal point are read from the main scale while the second digit after the decimal point is read from the vernier scale (sliding scale). This is the point or mark that coincides with that of the main scale.