Electric Charges SS1 Physics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Electric Charges
ELECTRIC CHARGES→ Production, Types, Distribution and Storage
Production of Charges
If a plastic pen is rubbed vigorously on the hair or a coat and it is held near a very small piece of paper, the paper will be attracted by the pen. Some substances are found to possess the ability to attract light objects once they are rubbed. The light object as well as the rubbed material are said to be charged or electrified with static electricity. Electrostatics is the study of charges at rest. It is a type of electricity that does not move from one point to another in the substance in which it is produced.
Types of Charges
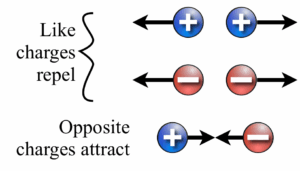
There are two types of charges: positive and negative charges.
Positive charge is obtained when a glass rod is rubbed with silk, or cellulose acetate with silk, while negative charge is obtained when an ebonite rod is rubbed with fur or polythene with fur. These two rods with positive and negative electrification attract each other when brought close. Repulsion occurs if two similar rods are brought close.
FUNDAMENTAL LAW OF ELECTROSTATICS
The law states that like charges repel, unlike charges attract.
Conductors And Insulators
Conductors are materials that allow electrons to pass through them easily.
Examples of conductors are metals, damp air, graphite, acids, salt solutions, the earth, and the human body.
Insulators are materials that do not allow electrons to pass through them easily. Examples of insulators are plastic, polythene, Bakelite, ebonite, paper, dry hair, silk, oils, glass, sulphur and wood.
Distribution of Charges
Experimental works have shown that charges are distributed where there is a sharp curve. The densities of these charges are greater at the surface of the sharp curve. The charge per unit area of a charged surface is called surface density.
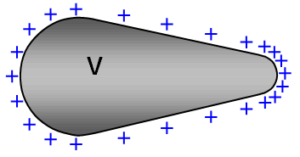
Charge Distribution is greater at the edge (sharp edge)
Storage of Charges
The electrophorus is a device for transferring and storing charges. It produces electric charges by electrostatic induction. Another device for the storage of electric charges is the capacitor
Gold Leaf Electroscope
The gold-leaf electroscope is an instrument used for testing positive and negative charges. It consists of a metal (brass) rod to which a thin gold leaf (or aluminium leaf) is attached. The rod is surmounted by a brass disc or cap and insulated from the metal case. The leaf is protected from outside influences (like drought) by enclosing it in an earthed metal case with glass windows.
Generally, the gold leaf can also be used to test the conducting properties of materials.
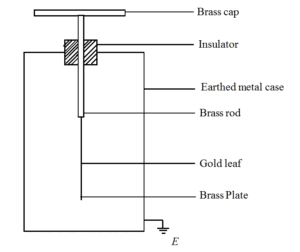
Diagram of gold-leaf electroscope
Uses of The Electroscope
- It is used to test whether a material is a conductor or an insulator. The material is made to touch the cap. Rapid collapse means that the charges escape easily and hence the material concerned is a good conductor. A slow collapse means that it is a poor conductor. No collapse means that it is an insulator.
- Use to test charges whether the charge is positive or negative. The gold leaves an electroscope to test the sign of the charge of an object. If an unknown charge is brought near to a charged electroscope and the leaf diverges more, the unknown charge is similar to the charge on the electroscope.
Charging An Insulated Body
A neutral insulated body can be charged by two methods:
- Contact method and
- By induction
- Contact Method: – The method is achieved by bringing a charged object in contact with it. By so doing the neutral insulated body acquired the same type of charge as that on the charged object.
- Induction Method: – This method is simply a process of charging a neutral body by placing a charged body near it without any contact between the two.
This process is explained in the following steps below:
- Bring a positive charge close to an insulated body to be charged. (Note: insulation as used here is by placing the body on an insulated stand to avoid the charge induced from leaking away). Negative charges on the insulated body are attracted towards the inducing charge while the positive charges are repelled away from it.
- Earth the insulated body by momentarily touching it so that the positive charge conducts away
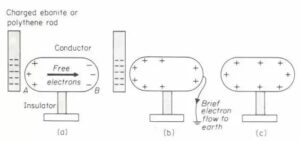
Diagram showing charging by induction
3. Remove inducing charge: From observation, the negative charge will spread around leaving the body as a negatively charged body. If the inducing charge is negative, then the body will acquire a negative charge after taking the steps above.
Lighting and Lighting Conductor
The atmosphere is known to contain ions or charged particles, which have been produced by radiation from the sun and by what is known as cosmic radiation, which enters the atmosphere from outer space.
Lighting is a sudden discharge or neutralizing of electric charges, and it occurs when charges build up in a cloud. The lighting conductors are long metal strips running from the spike end of a conductor on the top of a building. They are used to prevent buildings from destruction when struck by thunder or lightning. The conductor is a long metal rod installed or connected to the earth using a cable. The sharp outer point of the top gains an induced charge opposite to that in the thundercloud. The charge ionizes the nearby air and the charged air molecules flow upwards from the point. This discharges the cloud before a lightning flash occurs.