The Earth’s Rotation SS1 Geography Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: The Earth’s Rotation
The Shape Of The Earth
The earth has a spherical shape. Its shape can also be described as GEOID.
Though we walk on a flat surface, it is almost like a sphere and it is slightly flattened at the two poles.
There are many facts to prove that the earth is spherical.
Size of the Earth
The Earth is the fifth largest planet in the solar system. The surface area of the earth is approximately 443 million square kilometres (197 million square miles). The earth has a polar diameter of about 12,722km and an equatorial diameter of about 12,762km. At the equator, the earth measures about 40,085km in circumference. The polar circumference is 39,955km. Its mean density is estimated to be 5.5 grams per cubic centimetre.
PROOFS OF THE EARTH’S SPHERICITY
- Circumnavigation of the Earth: Ferdinand Magellan and his crew sailed around the world between 1519 and 1522 and came back to their starting point. Since then, several other people have done so thereby confirming the fact that the earth is not flat but spherical. If the Earth was flat, they would have met an abrupt edge thereby falling off.
- Sunrise and Sunset: Different parts of the world experience sunrise and sunset at different times. If the earth were flat, the sun would rise and set at the same time for all places. Note that the Earth rotates from west to east, so places in the east see the sun first before places in the west. The sun is said to rise in the east and set in the west.
- Aerial Photographs: Photographs of the earth taken from high altitudes by rockets show that the earth is spherical. This is the most recent proof of the sphericity of the earth.
- The Lunar Eclipse: During a lunar eclipse, the Earth casts a circular shadow on the moon. Only a sphere, like the Earth, can cast such a circular shadow.
- Ships Visibility: When a ship approaching a port is viewed, the top of the mast is seen first before the hull and later the rest of the ship’s body. In the same way, if a ship leaves a harbour, it disappears gradually. If the earth is flat, the ship from a distant view would appear and disappear at once.
- Shape of other Planets/Planetary Bodies: When the sun, moon, stars and other planetary bodies are viewed from any angle, they are all circular in outline. So the earth cannot be an exception.
- Experimental Proof/ Engineer Surveys/Driving Poles of Equal Length: Three poles of equal length driven at the same depth in a level ground were found to have the centre pole projected slightly above the poles at either side because of the curvature of the earth. If the earth was flat, all the poles would have been at the same height
MOVEMENT OF THE EARTH
It is the earth on which we stand that is constantly in motion. It revolves around the Sun and turns its different sides to the Sun at different times. When the sun emerges, we say the sun is rising and when the sun recedes, we say the sun is setting. Earth’s movement can be grouped into two: The Rotation of the earth and The Revolution of the earth.
THE ROTATION OF THE EARTH
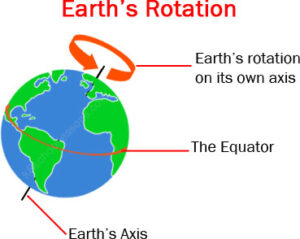
The rotation of the earth is the movement of the earth on its axis. By turning its axis from the west to the east, the earth makes a complete rotation i.e. it rotates through 360° in every 24 hours which makes a day. We should note that the earth rotates through 15o in 1 hour or through 1o in 4 minutes.
EFFECTS OF EARTH ROTATION
- Day and Night: As the earth rotates, only one part of the earth’s surface facing the sun receives the rays of the sun and experiences day, while the other part of the earth backing the sun experiences darkness(night).
- Time Differences From Place To Place: It causes differences in local time between places as the earth rotates from west to east, it means that for every 15° we go eastward, the local time is advanced by 1hr and for every 15° westward, the local time is behind by 1 hour.
- Apparent Sunrise and Sunset: During the rotation of the earth, the part that emerges from darkness into the rays of the sun experiences sunrise, while the part moving away from the sun rays experiences sunset. It thereby causes apparent sunrise and sunset.
- Deflection of Wind and Ocean Current: The earth’s rotation causes freely moving objects e.g. wind and ocean currents to deflect to the right. This deflection is in a clockwise direction when the object lies in the northern hemisphere and it is an anticlockwise direction for an object lying in the southern hemisphere.
- Daily Rising and Falling of the Tide: This is the rising and falling in the level of water in Seas and Oceans. This takes place twice every day.
ASSIGNMENT
- Explain the term earth rotation.
- Mention three effects of the earth’s rotation.
- The earth rotates on its own ______.






















