Gears JSS2 Basic Technology Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Gears
GEARS
A gear or cogwheel is a rotating machine part having cut teeth, or cogs, which mesh with another toothed part to transmit torque. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears almost always produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their gear ratio, and thus may be considered a simple machine. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a transmission. A gear can mesh with a linear toothed part, called a rack, thereby producing translation instead of rotation.
The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a cross-belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is that the teeth of a gear prevent slippage.
When two gears mesh, if one gear is bigger than the other, a mechanical advantage is produced, with the rotational speeds and the torques of the two gears differing in proportion to their diameters.
In transmissions with multiple gear ratios—such as bicycles, motorcycles, and cars—the term “gear” as in “first gear” refers to a gear ratio rather than an actual physical gear. The term describes similar devices, even when the gear ratio is continuous rather than discrete, or when the device does not contain gears, as in a continuously variable transmission.
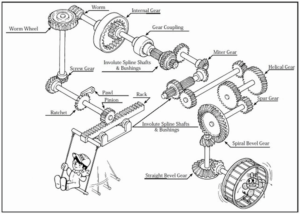
Gear types
Gg
Spur Gears
The most common and easy-to-produce parallel shaft cylindrical gears. Of a pair of gears, the larger one is called a gear and the smaller one a pinion.
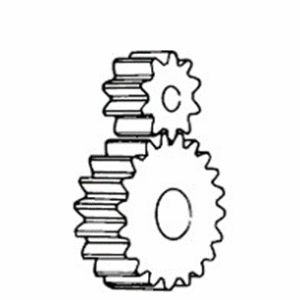
Helical Gears
Quiet and able to transmit larger torque than spur gears. Cylindrical gears with spiral-shaped tooth traces.
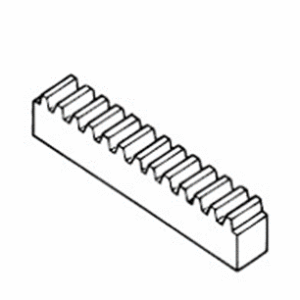
Gear Rack
Changes rotary motion to linear motion. A set consisting of rectangular or circular rod-shaped gear with mating small gear.
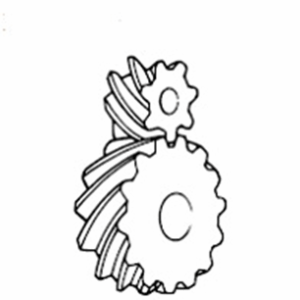
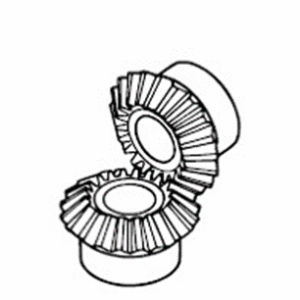
Bevel Gear
These cone-shaped gears are used in intersecting shaft applications. There are also bevel gears with spiral-shaped tooth traces called spiral bevel gears.
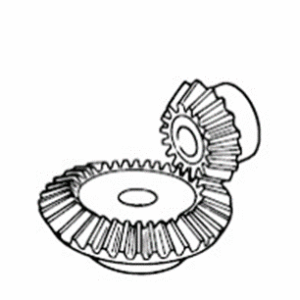
Spiral Bevel Gear
These cone-shaped gears are used in intersecting shaft applications. There are also bevel gears with straight-shaped tooth traces called straight bevel gears.
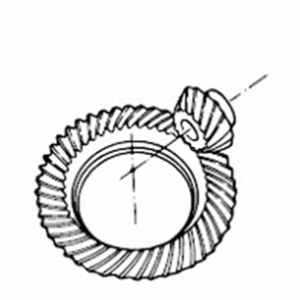
Screw Gear
Used in offset shaft application. Shape-wise, they are the same as helical gears.
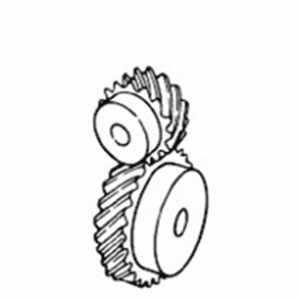
Miter Gear
Type of bevel gears in which the pair is made of the same number of teeth and used where speed reduction or increase is not needed.
Worm Gear
Used when a large speed reduction is needed. Worm and worm gear set. Normally, different materials are used for worm and worm gear.
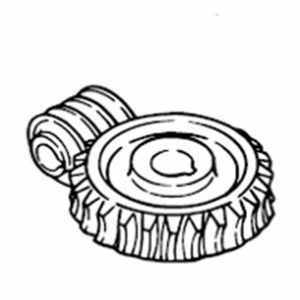
Internal Gear
Gear teeth are cut on the inside surface of hollow cylindrical forms and used in planetary gear systems. The gear teeth are cut using gear shaper machines.
QUESTIONS
- Define gear
- Mention 5 types of gear