Drawing And Shading SS1 Visual Arts Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Drawing And Shading

DRAWING
Drawing is the act of creating images or lines on a surface, usually paper, using various tools such as pencils, pens, markers, or charcoal. It is a form of visual expression and communication, that allows artists to convey ideas, emotions, and observations through a range of techniques and styles.
Drawing involves:
- Line: Creating contours, outlines, and shapes using various lines (straight, curved, diagonal, etc.).
- Shape: Defining forms and objects using geometric or organic shapes.
- Value: Creating light and dark areas to convey depth, volume, and texture.
- Texture: Suggesting surface quality through hatching, cross-hatching, stippling, or other techniques.
- Proportion: Ensuring accurate relationships between elements.
- Perspective: Creating a sense of space and distance.
Drawing can be used for:
- Artistic expression
- Communication (technical drawing, illustration)
- Observation (study, sketching)
- Design(planning, prototyping)
- Storytelling (comics, cartoons)
There are many drawing techniques, including:
- Realism
- Abstraction
- Cartooning
- Caricature
- Impressionism
Remember, drawing is a skill that can be developed with practice, patience, and dedication.
TYPES OF DRAWING:
Here are some common types of drawing:
- Realistic Drawing: Accurate and detailed representation of subjects.
- Cartooning: Exaggerated and simplified drawings for humour or storytelling.
- Caricature: Distorted and comedic drawings emphasizing facial features.
- Illustration: Drawings created for publications, products, or advertisements.
- Sketching: Quick, informal drawings for practice or observation
- Abstract Drawing: Non-representational drawings focusing on colour, shape, and form.
- Technical Drawing: Precise drawings for engineering, architecture, or design.
- Comic Art: Drawings for comics, graphic novels, or manga.
- Concept Art: Drawings for film, video games, or animation development.
- Portrait Drawing: Drawings focusing on the human face and expression.
- Landscape Drawing: Drawings depicting natural scenery and environments.
- Still life Drawing: Drawings of inanimate objects and compositions.
- Figure Drawing: Drawings of the human body and anatomy.
- Gesture Drawing: Quick drawings capturing movement and gesture.
- Imaginative Drawing: Drawings from imagination, fantasy, or creativity.
These categories often blend or overlap, and many artists explore multiple styles and techniques in their work.
SHADING
Shading is a drawing technique used to create the illusion of three-dimensional form and volume on a flat surface. It involves creating a range of values (light and dark areas) to suggest the shape, texture, and depth of an object or subject.
Shading can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Hatching: Closely spaced parallel lines that follow the contours of the subject.
- Cross-hatching: Layers of hatching lines at different angles to create texture and depth.
- Stippling: Small dots that create texture and value.
- Gradation: Smooth transitions from light to dark values.
- Atmospheric perspective: Shading that suggests depth and distance by fading objects into the background.
Shading helps to:
- Create volume and form
- Suggest texture and surface quality
- Indicate light sources and direction
- Enhance depth and dimensionality
- Guide the viewer’s eye through the composition
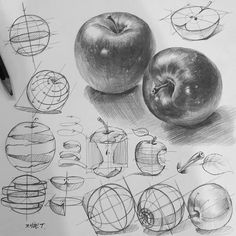
TYPE OF SHADING
There are different types of shading, including:
- Linear Shading: Using lines to create shading, including hatching, cross-hatching, and stippling.
- Tonal Shading: Using values (light and dark) to create shading, often with gradations.
- Color Shading: Using colours to create shading, often with gradual transitions.
- Hatching: Closely spaced parallel lines that follow the contours of the subject.
- Cross-Hatching: Layers of hatching lines at different angles to create texture and depth.
- Stippling: Small dots that create texture and value.
- Gradation: Smooth transitions from light to dark values.
- Atmospheric Perspective: Shading that suggests depth and distance by fading objects into the background.
- Flat Shading: Using solid colours or values to create flat, two-dimensional shading.
- Gouraud Shading: A smooth, continuous shading technique used in computer graphics.
- Cel Shading: A stylized shading technique using bold lines and flat colours.
- Sfumato: A subtle, soft shading technique creating a hazy or atmospheric effect.
These types of shading can be used alone or in combination to achieve various artistic effects and moods.















