Quadrilaterals JSS2 Basic Technology Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Quadrilaterals
QUADRILATERALS
A quadrilateral is a simple closed figure with four sides.
Types of quadrilaterals
There are five types of quadrilaterals.
- Parallelogram
- Rectangle
- Square
- Rhombus
- Trapezium
One common property of all quadrilaterals is that the sum of all their angles equals 360°.
Let us look into the properties of different quadrilaterals.
Parallelogram
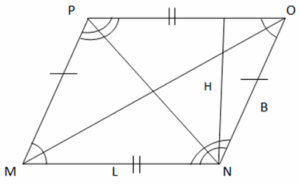
Properties of a parallelogram
- Opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
- Opposite angles are congruent.
- Adjacent angles are supplementary.
- Diagonals bisect each other and each diagonal divides the parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
- If one of the angles of a parallelogram is a right angle then all other angles are right and it becomes a rectangle.
Important formulas of parallelograms
- Area = L * H
- Perimeter = 2(L+B)
Rectangles
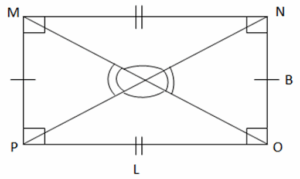
Properties of a Rectangle
- Opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
- All angles are right.
- The diagonals are congruent and bisect each other (divide each other equally).
- Opposite angles formed at the point where diagonals meet are congruent.
- A rectangle is a special type of parallelogram whose angles are right.
Important formulas for rectangles
- If the length is L and the breadth is B, then
Length of the diagonal of a rectangle = √(L2 + B2)
- Area = L * B
- Perimeter = 2(L+B)
Square
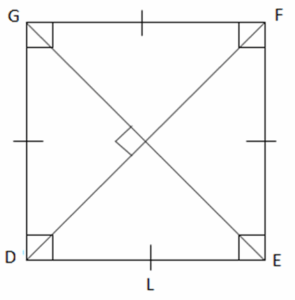
Properties of a square
All sides and angles are congruent.
Opposite sides are parallel to each other.
The diagonals are congruent.
The diagonals are perpendicular to and bisect each other.
A square is a special type of parallelogram whose all angles and sides are equal.
Also, a parallelogram becomes a square when the diagonals are equal and right bisectors of each other.
Important formulas for Squares
If ‘L’ is the length of the side of a square then the length of the diagonal = L √2.
Area = L2.
Perimeter = 4L
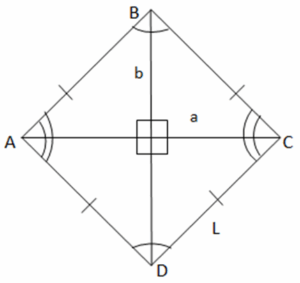
Rhombus
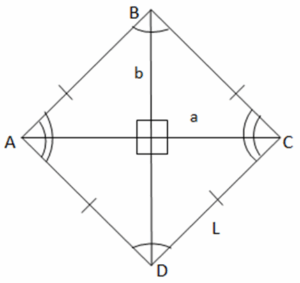
Properties of a Rhombus
- All sides are congruent.
- Opposite angles are congruent.
- The diagonals are perpendicular to and bisect each other.
- Adjacent angles are supplementary (For eg., ∠A + ∠B = 180°).
- A rhombus is a parallelogram whose diagonals are perpendicular to each other.
Important formulas for a Rhombus
If a and b are the lengths of the diagonals of a rhombus,
- Area = (a* b) / 2
- Perimeter = 4L
Trapezium
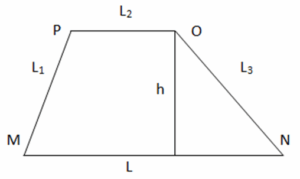
Properties of a Trapezium
- The bases of the trapezium are parallel to each other (MN ⫽ OP).
- No sides, angles and diagonals are congruent.
Important Formulas for a Trapezium
- Area = (1/2) h (L+L2)
- Perimeter = L + L1 + L2 + L3
Summary of properties
Summarizing what we have learned so far for easy reference and remembrance:
| S.No. | Property | Parallelogram | Rectangle | Rhombus | Square |
| 1 | All sides are congruent | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 2 | Opposite sides are parallel and congruent | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 3 | All angles are congruent | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | ✓ |
| 4 | Opposite angles are congruent | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 5 | Diagonals are congruent | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | ✓ |
| 6 | Diagonals are perpendicular | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 7 | Diagonals bisect each other | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 8 | Adjacent angles are supplementary | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Assignment
- Define quadrilaterals
- Define polygon













