Inequalities SS3 Further Mathematics Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Inequalities
Performance Objectives Students should be able to:
- Solve quadratic inequalities
- Solve inequalities in two dimensions.
Content
Quadratic Inequality
A quadratic inequality is an inequality in which one side is a quadratic polynomial and the other side is zero.
A quadratic inequality can take any of the following forms:
- ax<sup>2</sup> + bx + c > 0
- ax<sup>2</sup> + bx + c < 0
- ax<sup>2</sup> + bx + c ≥ 0
- ax<sup>2</sup> + bx + c ≤ 0
Quadratic inequalities are a type of algebraic inequality that involves quadratic expressions. A quadratic inequality looks like ax2+bx+c>0, ax2+bx+c<0, ax2+bx+c≥0 or ax2+bx+c≤, where a, b, and c are constants, and a≠0.
It is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus. They involve expressions containing quadratic polynomials and inequality signs. It is often required in solution sets that fulfill specific criteria. Lets know more about Quadratic Inequalities in detail below.
Quadratic Inequalities
Quadratic Inequalities are mathematical expressions involving quadratic equations that contain inequality symbols such as ≠, <, >, ≤, or ≥. They are represented in the form ax2 + bx + c < 0, > 0, ≤ 0, or ≥ 0, where ‘a’, ‘b’, and ‘c’ are constants, and ‘x’ is the variable raised to the power of 2.
These inequalities present relationships between quadratic functions and describe regions or intervals where the quadratic expression is less than, greater than, less than or equal to, or greater than or not equal to a specified value. Solving quadratic inequalities involves determining the sets of values for which the given inequality holds, considering various algebraic methods and graphical interpretations. If there is an equal to sign present we call it an Equation.
Quadratic Inequalities Definition
An expression where a quadratic expression ax2 + bx + c is equated to any variable of degree 2 or less or number with an inequality symbol such as ≠, <, ≤, >, ≥ is called Quadratic Inequality. For Example – 3×2 + 2x ≥ 0
Standard Form of Quadratic Inequalities
A quadratic inequality can assume any of the following standard forms:
- ax2 + bx + c > 0
- ax2 + bx + c < 0
- ax2 + bx + c ≥ 0
- ax2 + bx + c ≤ 0
How to solve Quadratic Inequality?
We can solve a Quadratic Inequality using the following steps:
Step 1. Set the quadratic expression: Write the quadratic inequality in the form ax2 + bx + c < 0, > 0, ≤ 0, or ≥ 0.
Step 2. Factor or find roots: Factorize the quadratic expression or use the quadratic formula to find the roots (if possible).
Step 3. Determine critical points: Identify critical points or values of ‘x’ where the inequality may change, considering the roots and the sign of ‘a’.
Step 4. Create intervals: Use critical points to create intervals on the number line, dividing it into sections where the inequality might change.
Step 5. Choose test values: Select test values within each interval to check the inequality’s validity. Use values like endpoints, zeros, or convenient numbers within each interval.
Step 6. Evaluate the inequality: Substitute the test values into the original inequality to determine if they satisfy the inequality.
Step 7. Determine solution regions: Identify intervals where the inequality holds based on the test values’ outcomes.
Step 8. Express solution set: Present the solution set either as an inequality on the number line or in set notation, considering the intervals where the inequality is valid.
Solve Quadratic Inequalities
Solving Quadratic Inequalities means finding the value of x for which it satisfies the given inequality. We can solve a Quadratic Inequality using three methods:
- Graphical Method
- Algebraic Method
Graphical Method
In Graphical Method, we first draw the graph of the inequality and then find the solution of the given inequality using the graph. Lets see how to solve Quadratic Inequalities using the Graphical method with the help of an example.
Example: x2 – 3x – 4 > 0
Solution:
We can solve the above example using graphical methods
Step 1: Plotting the graph of the quadratic function y = x2 – 3x – 4
Finding the x-intercepts:
Given quadratic function: y = x2 – 3x – 4
To find the roots, solve for y = 0:
x2 – 3x – 4 = 0
Factorizing the equation or using the quadratic formula:
x2 – 4x + x – 4 = 0
x(x – 4) + 1(x – 4) = 0
(x – 4)(x + 1) = 0
Therefore, the roots are x = 4 and x = -1
Plotting the graph:
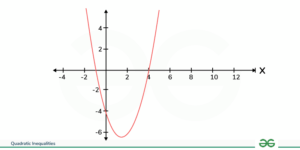
Step 2: Identifying regions where the graph lies above the x-axis (where y > 0)
We are looking for the regions where the quadratic function is positive (y > 0).
The function is y = x2 – 3x – 4. We know the roots are x = 4 and x = -1.
Step 3: Determining the x-values within these regions to obtain the solution set
Based on the graph, the regions where y > 0 are:
– x < -1
– x > 4
Therefore, the solution set for x2 – 3x – 4 > 0 is x < -1 or x > 4.
This solution is derived from observing the parts of the graph where the quadratic function y = x2 – 3x – 4 is above the x-axis.



















