Food Storage SS2 Biology Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Food Storage
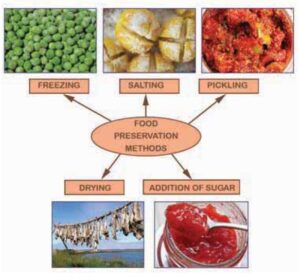
METHODS OF FOOD PRESERVATION (STORAGE)
The methods and principles of preserving food include:
- Salting: This involves coating the food with table salt or common salt (NaCl).
Principle: The salt on the surface of the food dehydrates it i.e. it removes water from the food.
This forms a highly concentrated solution which has more osmotic pressure than the cytoplasm of the microorganisms that cause decay. The salts inhibit the growth of the microbe or kill them. This method can be used for fresh meat, fish etc.
- Drying: Food such as vegetables, maize, cassava, fish, meat etc. can be preserved by drying under the sun.
Principle: Drying reduces the water content of the food thus making it unsuitable for the growth of spoilage microorganisms due to the increased osmotic concentration of food.
- Smoking: Involves placing the food over the naked fire to dry it. Food preserved this way includes meat, fish, groundnut, plantain etc.
Principle: The smoke creates an oxygen-deficient environment that kills microorganisms. The smoke also contains chemicals that are poisonous to the organisms.
- Refrigeration/Freezing: This involves keeping food in the refrigerator or freezer at low temperatures. Such food includes fruit, vegetables, milk, bread, fish, meat etc. Low temperature reduces the metabolic rate of microbes. Some can even be killed thus reducing spoilage considerably.
- Pasteurization: This is the heating of some food product to a very high temperature (72°C) for about 10 minutes and its immediate cooling for storage. The high temperature destroys the spoilage microbes. Milk, cheese, and beef can be preserved this way. Pasteurization usually precedes canning or bottling methods of food preservation.
- Canning/Bottling: This is the storage or sealing of processed and consumable food in cans or bottles under special conditions for future consumption. This is used for food like fruit, meat, fish, and beans. Etc. Microbes are gradually killed, the entrance of new ones is prevented and long storage is ensured.
- Irradiation: This is the subjection of some food e.g. Milk, Canned food, tubers, fruit juices etc, to a high radiation such as ultraviolet rays. The irradiation kills the microbes in the food and also prevents the entrance of new ones.
- Chemicals: This is the addition of harmless chemicals to food e.g. soft drinks, vegetables etc.
Principle: The chemical choke spoilage organisms in the food. It also dehydrates or toxicates the microbes.
EFFECTS OF FOOD STORAGE ON THE POPULATION
- Prevention Of Hunger And Famine: Hunger or famine that would have resulted from food shortage is averted with the preservation of food.
- Maintenance Of Stable Price: During harvest, food is cheap. However, food storage ensures the availability of food throughout the year. This helps in the maintenance of stable prices.
- Reduce the effect of natural disasters, floods, earthquakes, pest attacks and even war that cause farm crop failure or destroy entrance farm activities. Food already stored etc. harvest will save people from starvation in the period of scarcity.
- Food storage employs workers, especially in food processing companies.






















