Database Management System SS1 Data Processing Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Database Management System
A database is an application that is used to store information in a structured way. It is a collection of records or data in an organized form.
A database management system is a collection of computer software that enables users to define, create and maintain a database. A database management system (DBMS) is a computer application that interacts with the user, other applications and the database itself to capture and analyse data. The general purpose of a database management system (DBMS) is designed to allow the definition, creation, querying and administration of a database. The DBMS serves as an interface between the database and end users or application programs, ensuring that data is consistently organized and remains easily accessible. Database Administrators are those that control the database system. They also control the access and security aspects of the database.
FUNCTIONS OF DBMS
A DBMS makes it possible for users to create, edit and update data in database files. The functions also include:
- Concurrent access to the same database at the same time.
- It creates security rules to determine the access rights of users.
- It improves the integrity of the data in the database.
- It also provides a data dictionary for description of data.
EXAMPLES OF DATABASE MANAGEMENT PACKAGES
There are various database management systems. Some of these are:
- Microsoft Access: It is a DBMS developed by Microsoft. It stores data in its format based on the access jet engine. It has the facilities like importing or linking directly to data stored in other databases.
- MySQL: It is an open-source DBMS. One of the most popular DBMS.
- Oracle: It is an object-relational database management system.
- Microsoft SQL server: It was developed by Microsoft. The primary function of this software is to store and retrieve the data as requested by other applications, whether those applications are on the computer or running on other computers across the network.
- Filemaker: It was begun as an MS-DOS-based computer program. It is a cross-platform relational database management system.
DATABASE TERMINOLOGIES:
- Rows: are the records.
- Column: is vertical and labelled alphabetically.
- Field: is a group of related characters in a file
- Character: a single symbol in a file.
- Record: is made of several fields that are related together and treated as an entity.
Database packages are used to design a database in a computer. An example of a common database package is Microsoft Access. MS Access is a Relational Database Management System used to create and modify databases.
USING MS- ACCESS FOR DATABASE
To create a database on the computer with MS Access
Load MS Access: do the following;
- Click on the Start Menu
- Point to All program
- Point to Microsoft Office
- Click on Microsoft Office Access
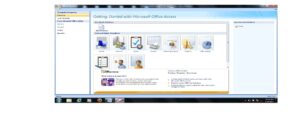
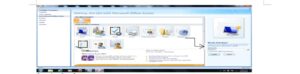
CREATING DATABASE
- From the displayed window, click on the blank database.
- By the right-hand side of the windows, where the arrow is pointing in the picture screen above, click inside the file name text box and type the desired database name.
- Click on the Create command button. A database with the filename given will be created
- Files are created as tables in the database
CREATING A FILE
- Click on the Create menu and select Table
- At the All Tables tab, right-click on any of the tables.
- Select Design View
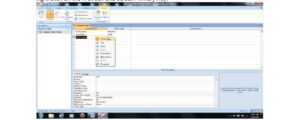
In the Save As dialogue box, type a desired table name (e.g. Student Table) in the Table Name text box and click ok.
Tables in a database on a computer are composed of rows and columns. A table in MS Access is organized into rows and columns like the picture screen shown below.
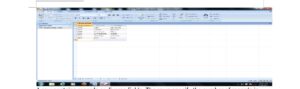
A row contains records or diverse fields. The rows specify the number of records in the table. For example, in the picture screen above, there are six records in the student table.
A column usually represents a field in a database table. It contains specific types of information. For example, in the picture screen above, there are three fields (data fields), REG. No., Surname, and first name.