Human Reproduction (II) JSS1 Basic Science Lesson Note
Download Lesson NoteTopic: Human Reproduction (II)
HUMAN REPRODUCTION (II)
Topics:
-
Pregnancy
-
Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy
-
Stages of Growth of the Fetus
Pregnancy (Conception)
Conception, also known as pregnancy, is the period between fertilization and the birth of the young one.
In humans, the period of pregnancy lasts for about nine (9) months.
Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy
-
Food Aversions:
A newly pregnant woman may feel repelled by the smell of certain foods or find that foods she once enjoyed now seem unpleasant. -
Mood Swings:
Due to hormonal changes, it is common for pregnant women to experience changes in mood. -
Abnormal Bloating:
Hormonal changes may cause bloating similar to premenstrual symptoms. -
Frequent Urination:
Hormonal changes increase blood flow through the kidneys, filling the bladder more quickly and leading to frequent urination. -
Fatigue:
Pregnant women often feel tired and sleepy due to changes in metabolism and hormones. -
Sore Breasts:
The breasts become swollen and sensitive due to rising hormone levels. -
Missed Period:
Missing a menstrual period is a common sign of pregnancy, though some women may still experience light bleeding. -
High Basal Body Temperature:
If body temperature remains elevated for 18 consecutive days, it could indicate pregnancy.
Care Needed During Pregnancy
-
Get a pregnancy test as soon as you miss your period.
-
Talk with your partner and someone you trust.
-
Begin antenatal care check-ups with a medical doctor.
-
Follow proper antenatal instructions and avoid unprescribed drugs.
-
Eat nourishing foods rich in protein, calcium, folic acid, iodine, and iron.
-
Drink plenty of water and fruit juices.
-
Get adequate rest.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption.
Myths and Facts About Pregnancy
A myth is a false belief that many people hold, while a fact is a truth that can be proven.
In many African societies, there are several myths about pregnancy that are not scientifically true.
Myths About Pregnancy
-
Only pregnancy can make a woman miss her period.
-
All pregnant women vomit.
-
Pregnancy makes a woman unclean before God.
-
All pregnant women have morning sickness.
-
Pregnant women should not dye their hair.
-
Pregnant women shouldn’t eat fish.
-
A woman cannot get pregnant during her period.
-
A woman cannot get pregnant the first time she has sex.
-
Washing the vagina after sex prevents pregnancy.
-
Pregnant women should not take baths.
Facts About Pregnancy
-
Pregnant women should not carry heavy objects.
-
Some women may experience light bleeding and still be pregnant.
-
Pregnant women should not change cat litter.
-
Pregnant women should not drink alcohol.
-
Some pregnancies can last longer than nine months.
Stages of Growth of the Fetus
Each month, a group of eggs (oocytes) develops in the ovary. Usually, one egg matures and is released during ovulation.
After fertilization, the fertilized egg (zygote) begins to divide and travel down the fallopian tube toward the uterus for implantation.
Once implanted, it develops into an embryo, and after the 8th week, it becomes a fetus.
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters, each showing distinct developmental stages.
Month-by-Month Fetal Development
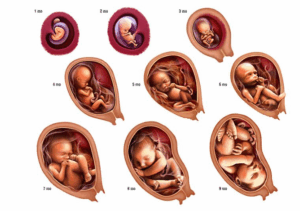
Month 1:
-
The amniotic sac forms around the embryo.
-
The placenta develops to supply nutrients.
-
The heart begins to beat (~65 times/min).
-
Length: about ¼ inch (smaller than a grain of rice).
Month 2:
-
Facial features and limbs start forming.
-
Neural tube (brain and spinal cord) develops.
-
The baby is about 1 inch long.
-
Heartbeat can usually be detected.
-
The embryo becomes a fetus by the end of the month.
Month 3:
-
Arms, hands, fingers, feet, and toes fully form.
-
Teeth and nails begin to develop.
-
Organs become functional.
-
Length: about 4 inches; weight: ~1 ounce.
Month 4:
-
Heartbeat audible with Doppler.
-
Hair, eyelashes, eyebrows, and nails form.
-
Nervous system begins to function.
-
Gender can be identified on ultrasound.
-
Length: about 6 inches; weight: ~4 ounces.
Month 5:
-
Baby starts moving (quickening).
-
Hair begins to grow; skin covered with vernix caseosa.
-
Length: ~10 inches; weight: ½–1 pound.
Month 6:
-
Skin is reddish and wrinkled; veins visible.
-
Eyelids open; responds to sounds.
-
May survive with intensive care if born prematurely.
-
Length: ~12 inches; weight: ~2 pounds.
Month 7:
-
Baby gains body fat; hearing fully developed.
-
Moves frequently and responds to stimuli.
-
Length: ~14 inches; weight: 2–4 pounds.
Month 8:
-
Brain development continues rapidly.
-
Can see and hear; lungs still maturing.
-
Length: ~18 inches; weight: ~5 pounds.
Month 9:
-
Lungs nearly fully developed.
-
Baby’s reflexes are well-coordinated.
-
Baby assumes birth position (head down).
-
Length: 18–20 inches; weight: ~7 pounds.
CLASSWORK 2
-
What is pregnancy?
-
Give four (4) facts about pregnancy.









